In this article:
A stroke occurs in the brain due to high blood pressure, a blood clotting disorder, or illegal drug abuse. It may or may not result in bleeding and is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. (1)
If you have one of the following conditions, you may be at risk of a stroke: (1)
- Low alertness and delayed responsiveness to stimuli
- Slurry language, repetition of words, and lack of fluency
- Weak motor response, dropping things, and weakness of grip
- Loss of visual clarity
- Facial muscle paralysis
A simple CT scan can diagnose a stroke, which is then classified into stages based on the severity of symptoms. Stroke treatment can vary based on age, presence of other illnesses, severity of symptoms, and other conditions. (1)
What Causes a Stroke?
The most common modifiable factor that can cause a stroke is high blood pressure. But other chronic conditions such as diabetes, obesity, high cholesterol levels, or long-term smoking can also increase the chances of developing a stroke. (2)
Other factors that can affect the risk of stroke but cannot be changed include age, gender, ethnicity, and genetics. (2)
How Can You Reduce the Risk of Strokes?
Modifiable factors can be managed using dietary and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of strokes.
1. Keep blood pressure in check
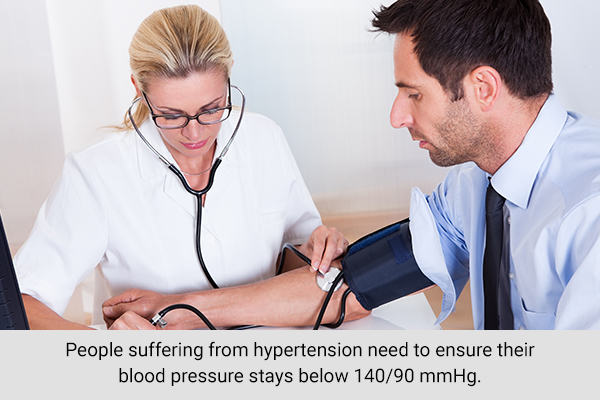
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a major factor for stroke, with almost half of the people with a stroke suffering from high blood pressure.
People with hypertension need to ensure their blood pressure stays below 140/90 mmHg. (3)
Mild hypertension can be maintained by reducing sodium intake to no more than 1.5 g daily, reducing intake of high-fat foods, including fiber-rich fruits and vegetables in the diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding drugs that can increase blood pressure. (4)
It is important to constantly check your blood pressure and ensure it stays below the recommended level.
2. Manage diabetes and its symptoms well
Diabetes is also a risk factor for developing heart diseases. Several studies have linked the presence of type 2 diabetes to stroke. (5)
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and reducing insulin resistance are of utmost importance. Consuming fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, opting for low-fat foods, and exercising daily are all part of the management strategy for type 2 diabetes. (5)
3. Reduce cholesterol levels
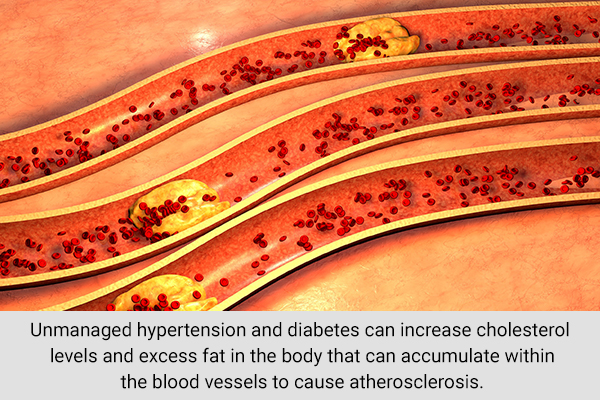
Unmanaged hypertension and diabetes can increase cholesterol levels, and the excess fat in the body can accumulate in the blood vessels, causing atherosclerosis.
There are mixed studies linking high cholesterol levels and the risk of stroke, with more recent ones suggesting high LDL (bad cholesterol) levels may cause nonbleeding strokes. (6)
High cholesterol levels can be managed by leading a healthy lifestyle that includes consuming a diet of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables. Exercising for at least 150 minutes each week and avoiding high-fat foods are also important. (7)
4. Increase physical activity
Low levels of physical activity can lead to overweight and obesity, which are considered the second most preventable leading cause of death worldwide. A diet high in fat and sugar, overeating, consuming highly processed foods, and low physical activity are all attributing factors to obesity. (8)
Weight management is critical for people with overweight and obesity to reduce their risk of stroke and associated complications. Strategic and tailored weight loss plans are beneficial as they take into account personal factors and challenges regarding dietary and lifestyle modifications. (9)
5. Reduce inflammation in the body

Inflammation in the body is a result of the body’s immune response to unmanaged chronic illness or foreign bodies. The substances generated as a result of inflammation can cause tissue injury and ultimately increases the risk of stroke. (10)
In addition, inflammation can cause body pain, tiredness, sleeplessness, depression and anxiety, stomach distress, weight gain, and frequent infections. (11)
Consuming foods that are anti-inflammatory is the best way to combat inflammation. (11) Anti-inflammatory foods include:
- High-fiber foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Low-fat foods
- Nuts and seeds
- Green and black tea
- Turmeric
- Omega-3 fatty acids from walnuts and fish oil
In addition, exercise is useful in reducing inflammation and preventing the risk of stroke and other diseases.
6. Limit alcohol consumption and avoid substance abuse
The relationship between alcohol consumption and the risk of stroke is a debated topic.
Some studies suggest low and moderate alcohol consumption (<2 drinks per week) reduces the risk of stroke; however, excessive alcohol (>4 drinks per week) can worsen it. (12)
Drug abusers also have an increased risk of stroke and other diseases. This is particularly worse for younger adults as drug abuse is more likely to be common in them. (13)
7. Avoid smoking

Smokers also have an increased risk of stroke as compared to nonsmokers, with 5 cigarettes per day increasing the risk by 12%. (14)
Studies have found passive smokers to have a 45% increased risk of stroke as well. (14) People suffering from chronic illness can also worsen their symptoms by smoking and are highly encouraged to quit.
Most-Asked Questions About a Stroke
Can a person recover after a stroke?
Recovery after a stroke depends on how severe the stroke had been and how long it took to diagnose. Oftentimes, a stroke may leave a person disabled. It is better to consult your doctor to identify a rehabilitation plan suited to your needs.
What foods should people who have suffered from a stroke avoid?
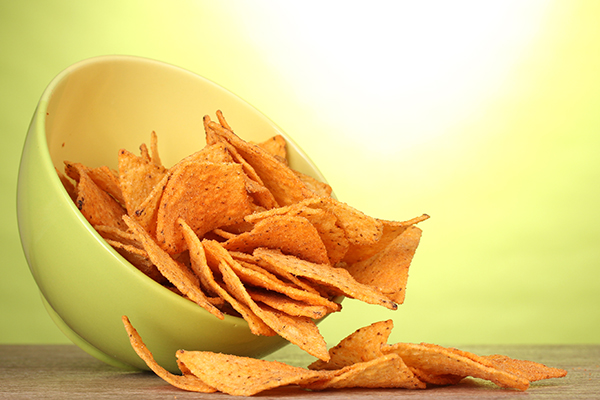

As discussed in this article, risk factors for stroke arise from the consumption of highly processed, high-salt, and high-fat foods. Chips, packaged foods, and ready-to-eat meals should generally be avoided.
Your focus should be on choosing high-fiber foods with healthy fats from nuts and seeds, whole-grain meals, and good-quality protein sources such as lean meats, legumes, beans, and pulses.
Final Word
A stroke is one of the most deadly occurrences that can leave a long-lasting impact on a person even after the incident. Common risk factors for stroke include high blood pressure and high body weight.
Modern Western diets with their high fat and high salt content can be very damaging to health. It is important to consume a healthy well-balanced diet abundant in fiber-rich foods and without added sugar to reduce the risk of strokes.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


