In this article:
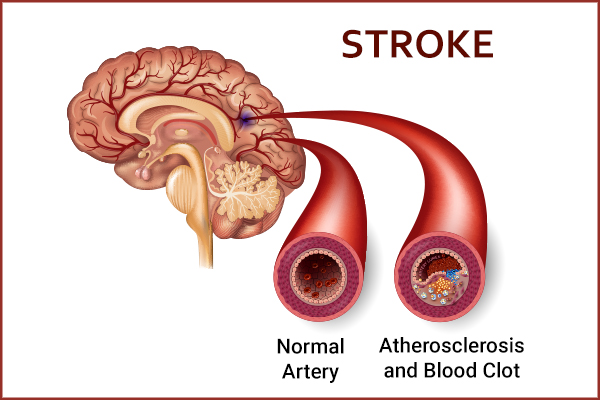
An ischemic stroke refers to brain damage caused by an interrupted blood supply. It is one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Commonly, strokes can be prevented with the help of blood thinners, especially for those with a cardioembolic origin.
This article talks about the use and risk of these blood thinners and tips with blood thinner use.
Blood Thinners for Stroke Prevention
Guidelines for stroke prevention currently include blood pressure reduction, statin therapy, anti-thrombotic therapy (blood thinners), and lifestyle modification. (1)
Blood thinners are first-line medicines that are used for the secondary prevention of ischemic stroke/transient ischemic attack. Blood thinners are subdivided into two categories based on their mode of action:
- Anticoagulants (2) (heparin or warfarin) prevent the body from making clots.
- Antiplatelet drugs (3) (aspirin, Clopidogrel) prevent platelets from sticking together and attaching to the blood vessel walls.
This article will focus on anticoagulants mainly. So, for the rest of the discussion, blood thinners = anticoagulants.
Warfarin is one of the most studied anticoagulants. There are newer anticoagulants, namely, direct oral anticoagulants (DOAC), which include non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants (NOAC) such as Pradaxa (dabigatran), Xarelto (rivaroxaban), and Eliquis (apixaban).
However, it is possible to have ischemic as well as hemorrhagic stroke even while on blood thinners due to cardioembolic (underlying atrial fibrillation) and non-cardioembolic mechanisms (large artery atherosclerosis, small vessel disease).
Subtherapeutic level (low INR) is the most common reason for stroke in patients taking warfarin. Missing doses, non-compliance, or under-dosing can lead to strokes in people taking DOAC. (4)
Usage of Blood Thinners After a Stroke

Patients who have had a cardioembolic stroke (irregular heart rhythm/atrial fibrillation, cardiomyopathy with low ejection fraction leading to left ventricular thrombus) will require life-long anticoagulation.
In addition, in some stroke patients, there may be other reasons to be on long-term anticoagulation such as acute coronary syndrome, prosthetic heart valve, venous thromboembolism, and hypercoagulable conditions.
Important Tips to Consider While on Blood Thinners

It is important to modify your lifestyle to prevent complications associated with a stroke and its medications.
- People taking warfarin need to limit their alcohol intake as it can increase the INR.
- People who are on anticoagulants need to be careful and are recommended to talk with their doctor before starting any new medications.
- Discuss safety with your doctor before undergoing any invasive procedure while being on anticoagulants.
- Always carry a patient info card/mediation card/medical alert bracelet with you as it will be useful in case of an emergency. (5)
- Patients taking warfarin need to be aware of the foods that are high in vitamin K as these food items can affect their metabolism. These include green, leafy vegetables, salad dressings, cranberries, and grapefruits.
- Caution is recommended even when taking some natural health food products and herbal remedies.
- The NOACs (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban) are usually not affected by any foods that you eat, so they do not need to be monitored as carefully. (5)
Side Effects of Blood Thinners
People who use blood thinners are at risk of bleeding in the brain (intracranial hemorrhage). It’s one of the most worrisome complications and is a medical emergency.
People with a previous history of stroke (especially intracerebral hemorrhage), hypertension, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, intracranial vascular anomaly, brain tumor, drug abuse, and tendency to fall are at a higher risk of bleeding complications.
The overall risk of intracranial bleeding is lower with DOAC treatment compared with warfarin. (6)
Is Coffee Considered a Blood Thinner?
Coffee may have an indirect effect on blood clot formation, according to a 2008 study published in the British Journal of Nutrition. (7) As of now, there is no further evidence or definitive recommendations for/against coffee being considered as a blood thinner.
Natural Ways of Preventing a Stroke

Healthy lifestyle choices can help prevent strokes. (8) These usually involve measures to control blood pressure and cholesterol levels, both of which contribute to an increased risk of stroke.
- Follow a healthy diet: It is recommended to consume fresh fruits and vegetables. Moreover, eating foods low in fat and cholesterol and high in fiber can help manage cholesterol levels in the body. Limiting sodium intake helps control blood pressure.
- Get physically active: Physical activity will help you to maintain a healthy weight and normal levels of cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Do not smoke: If you do smoke, quitting will lower your risk of stroke.
- Limit alcohol: Avoid drinking too much alcohol, which can raise your blood pressure.
- Manage stress: Practice relaxation techniques to reduce tension in your mind and body.
- Avoid illicit drugs: Recreational drugs such as methamphetamines and cocaine increase the risk of stroke.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can cause the blood to thicken, thus increasing the risk of blood clots. Therefore, it is important to stay hydrated to prevent strokes. (9)
Is Stroke Curable?
Time is brain. Stroke is a medical emergency! If the patient does not get treatment promptly, he/she is more likely to have permanent brain damage.
Conversely, timely treatment of stroke can help minimize the damage and complications, enabling proper recovery. Therefore, it is imperative to get the patient to the hospital in time, as a few minutes can make the difference between life and death in the case of a stroke.
Final Word
Blood thinners are medications that help prevent clot formation, and help prevent strokes. Since they have risk of bleeding complications, you must consult a doctor about suitable use.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


