In this article:
Mumps is an acute, self-limited, highly contagious viral illness that typically causes swelling of the salivary glands located in front of the ear, near the jaw. Thus, mumps is characterized by a tender, swollen jaw.

What Causes Mumps?
Mumps is caused by a virus called the paramyxovirus, which is an RNA virus and a member of the rubulavirus family.
Different Stages of Mumps
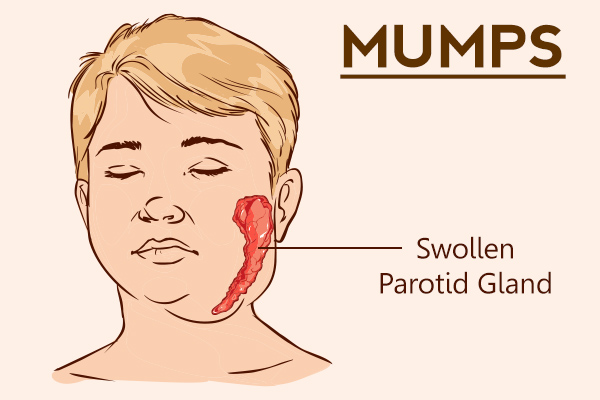
The initial non-specific symptoms of mumps (low-grade fever, headache, fatigue, malaise, and low appetite) are followed by parotid gland swelling on one side, which usually develops on the third day of illness.
Recurrent parotitis, on the other side, can develop days to weeks later.
General Signs and Symptoms of Mumps
Signs and symptoms of mumps can be anywhere from mild to severe. Some individuals can be asymptomatic and not even know they are sick with mumps.
- Mild symptoms of mumps look very much like a common cold (fever, headaches, body aches, weakness, fatigue, and loss of appetite). (1)
- The distinguishing sign of mumps is parotitis, which is swelling of the salivary glands.
- In some rare cases, mumps can cause severe complications such as meningitis, encephalitis, deafness, and orchitis.
Standard Line of Treatment

Treatment for mumps is mainly supportive, which means it aims to relieve the symptoms rather than curing the infection.
Like all other viral infections, this one also resolves on its own after running its course. But getting plenty of rest and drinking lots of fluids can help accelerate the recovery process.
How Helpful Are Vaccines in Treating Mumps, and Which Vaccine Should Be Used?
The best way to decrease your risk of getting mumps is by getting vaccinated. The mumps vaccine is part of two combination vaccines:
- Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccine
- Measles, mumps, rubella, varicella (MMRV) vaccine
These vaccines are very safe and effective. Most children don’t get any side effects. The side effects that can occur are very mild, such as a low-grade fever or rash. Discuss with your doctor about which combination vaccine is the right choice for you or your child.
Is One Dose of Mumps Vaccine Enough for a Lifetime?
Having two doses of the vaccine provides better immunity. The MMR and MMRV vaccines are given in two doses in children. The first dose is usually given at 12 through 15 months of age, and the second dose is given at 4 through 6 years of age. (2)
The mumps component of the vaccine is about 78% effective after one dose and 88% effective after two doses. So, people with only one dose of the vaccine are at higher risk of getting mumps than those with two doses. (2)
Unvaccinated adults should get two doses of the MMR vaccine 28 days apart. During a mumps outbreak, a third dose of the mumps vaccine may be required for at-risk individuals.
Is This a Recurrent Infection?
Being infected with mumps once means you’ll never have them again. It takes a single infection with the mumps virus for your body to become permanently immune to it.
Duration of the Mumps Infection
Most cases of mumps resolve within 1–2 weeks, whereas the swelling in the salivary glands generally lasts for 2 days, but can extend for as long as 10 days. (3)
Home Remedies for Symptomatic Relief
Mumps is a self-limited disease, and the treatment is mainly supportive, which includes optimum fluid intake and rest. There isn’t much you can do to shorten the duration of the infection, but there are some home care measures that can help ease its symptoms.
These include the application of cold compresses over the swollen jaw or gland area and the use of over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen to relieve fever and pain.
Is Mumps Contagious?
Mumps is a highly contagious disease. It spreads via direct contact with saliva or respiratory droplets from the mouth, nose, or throat of the infected person.
- When a mumps patient coughs, sneezes, or talks, these droplets are released in the air and can be inhaled by anyone in the vicinity.
- You can also contract the infection by sharing utensils with an infected person.
- Close-contact activities such as playing sports, dancing, or kissing can also transmit the virus more easily.
The infectious period begins a few days before the salivary glands begin to swell and can last up to 5 days after the swelling begins. (3)
Risk Factors for Contracting Mumps
The following groups are more susceptible to mumps than others:
- Anyone born during or after 1957 who has never had mumps or has never been vaccinated (4)
- People of all ages can get this infection, but children between 2 and 12 years old have the highest risk
- International travelers to countries with a high prevalence of mumps
- College students living in close proximity with others
- People with compromised immune systems (such as those undergoing chemotherapy or receiving immunosuppressive drugs)
Potential Complications Related to Mumps

Complications of mumps are rare but can be very serious. These include:
- Orchitis, which is the swelling of one or both testicles in post-pubertal males, is very painful and, in rare cases, can lead to sterility in men (inability to have children).
- Encephalitis and meningitis are inflammation of the brain and can lead to long-lasting neurological problems and death.
- Pancreatitis causes pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, and vomiting.
- Hearing loss in one or both ears can be permanent.
- Miscarriage may occur, especially early in pregnancy.
Final Word
Mumps is a very contagious virus, and it can spread easily in crowded environments such as daycares, classrooms, and college dorms. The initial phase of the disease can look like a common cold. Although it’s a self-limited illness, it can lead to long-term health consequences.
The best way to protect yourself and your child from getting mumps is by getting vaccinated. Vaccinations are not 100%, but they do greatly reduce the risk of getting mumps.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


