In this article:
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD) spread by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It mainly affects the moist and warm body areas such as the throat, eyes, vagina, anus, urethra, and reproductive tract of women. (1)

The infection spreads from person to person through sexual contact. Both men and women can contract the disease. The high-risk group includes people who have multiple partners. Children of infected mothers can contract the disease during childbirth.
According to the World Health Organization, gonorrhea mostly affects women of reproductive age (between teenage years and menopause). (2)
In 2021, more than 700,000 cases of gonorrhea are reported annually in the United States, making it the second-most common STD in the country. Rates of reported gonorrhea have increased by 118% since their historic low in 2009. (3)
Symptoms of Gonorrhea
It usually takes about 2 weeks for the symptoms of gonorrhea to appear, after contact with the bacterium. The symptoms in men include painful urination, pus and discharge from the penis, swelling or redness in the opening of the penis, persistent sore throat, and swelling or pain in the testicles.
In women, the symptoms include painful urination, vaginal discharge, frequent urination, pain in the abdomen, pain during intercourse, heavy periods, sore throat, and fever.
Treatment usually involves the use of antibiotics. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to other health issues and infertility in men and women.
Treatment for Gonorrhea
Antibiotics are used for the treatment of gonorrhea. At present, the most commonly used antibiotic is cephalosporin ceftriaxone along with azithromycin. However, due to emerging drug-resistant strains of N. gonorrhoeae, more options are being explored. (4)
The steps being taken to develop new therapies for treating drug-resistant gonococcal infections are:
- Trying out new combinations of known antibiotics
- Trying to develop novel antibiotics
- Use of alternative therapies
Among the existing antibiotics that can be used as alternatives to cephalosporin, gentamicin in combination with azithromycin has proven to show good results in the treatment of genital gonorrhea, according to a clinical trial reported in The Lancet. (5)
Alternative therapies and lifestyle changes focus on preventing and controlling the infection and getting rid of it before it can develop resistance.
The most common treatment method followed by doctors is:
- A course of antibiotics (usually ceftriaxone or cefixime)
- Treatment of the sexual partners of the patient
- Additional therapy for complications
Diagnosis of Gonorrhea
For diagnosis, your doctor will test for the bacteria in samples obtained by a swab of the affected area, such as the urethra, rectum, vagina, or throat, or a urine sample collected for testing. (1)
Alternative Therapies for Dealing With Gonorrhea
Many herbal remedies are available to treat gonorrhea, and here are some of them.
1. Incorporate garlic into your diet
Garlic has antibacterial properties that are attributable to an ingredient called allicin. Aqueous extracts of garlic have been shown to inhibit the growth of N. gonorrhoeae. (6)
Hence, use garlic in your regular cooking or add it to your soups, gravies, and curries. Alternatively, eat 2 or 3 cloves of garlic on an empty stomach daily. This will help in boosting the immunity of your body.
2. Rose periwinkle root can help
The root of rose periwinkle (Catharanthus roseus) has been shown to have antibacterial properties and has been used traditionally by the Bapedi people of Africa to treat gonorrhea. (7)
The treatment regimen used by traditional Bapedi healers involved a 7-day three-times-a-day procedure to be effective.

3. Try using tulsi herb
A 2021 review in Frontiers in Pharmacology has reported on the inhibitory effect of a chloroform extract of tulsi (Ocimum sanctum) on N. gonorrhoeae. (8) The inhibitory effect may be attributed to the presence of eugenol in tulsi. (9)
4. Consume Barbados nut
Barbados nut (Jatropha curcas), also called physic nut and ratanjot, is not only an ornamental plant but also a medicinal plant. It has been used in traditional medicine to treat various infections including gonococcal infections. (10)
An earlier study reported that the hexane extract of the roots of J. curcas inhibit the growth of N. gonorrhoeae and showed results comparable to those obtained with gentamycin. (11) The inhibitory effect was attributed to the presence of steroids, alkaloids, and tannins in the extract. (12)
5. Betel can prove beneficial
Betel (Piper betle L.) is a vine and is commonly known as paan in India. It has been traditionally used to treat gonorrhea in Chinese and Moroccan medicine. (13) Its medicinal activity may be attributed to the presence of terpenes.
6. Use Gale of the wind plant
Gale of the wind (Phyllanthus niruri) is a leafy herbal plant and is called bhumyamalaki in India. It has been used in the treatment of gonorrhea in traditional Indian medicine. (14)

7. Consume turmeric
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is a bright-yellow spice belonging to the ginger family. Its rhizome is used in cooking.
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with medicinal properties. According to a 2014 report, a derivative curcumin FM0187 has a potent inhibitory effect against N. gonorrhoeae. (15)
8. Thorny nightshade can aid in relief
The thorny nightshades S. xanthocarpum and S. pseudocapsicum possess saponins, a class of compounds with antibacterial properties, and have been used in traditional Asian medicine to treat gonorrhea. (16)
9. Give neem a try
Neem (Azadirachta indica) has many medicinal properties on account of its many phytochemicals, including azadirachtin, nimbolinin, quercetin, and sitosterol. (17) Hence, neem is a potent antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor agent.
Neem has been used in traditional Indian Ayurvedic medicine in the treatment of gonorrhea. (18)

10. Use Listerine
Studies were conducted on the use of Listerine among male homosexuals, and the results indicated that it has an inhibitory effect on the gonococcal infection on the pharyngeal surface. Therefore, Listerine may be used to control gonorrhea in male homosexuals. (19)
How Can Gonorrhea Be Prevented?
It is important to practice safer sex and use protection to prevent STDs. Latex condoms, when used consistently and correctly, can reduce the risk of transmission of gonorrhea. (20)
How to Avoid the Transmission of Gonorrhea to Others?
Avoid having intercourse until you have finished treatment and gotten re-tested to ensure you are free of the infection. Make sure your sexual partners also get treated for gonorrhea.
Most-Asked Questions About Gonorrhea
How long does it take for gonorrhea to infect the whole body?
Inmen, it usually takes 2–7 days after infection for the symptoms to appear. Sometimes, it can take up to a month for symptoms to manifest. Often, most people are asymptomatic – 10%–15% of men and 80% of women do not exhibit any symptoms.
Can gonorrhea recur?
Yes, it can recur if you have sexual contact with an untreated partner or a new partner.
What is Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome?
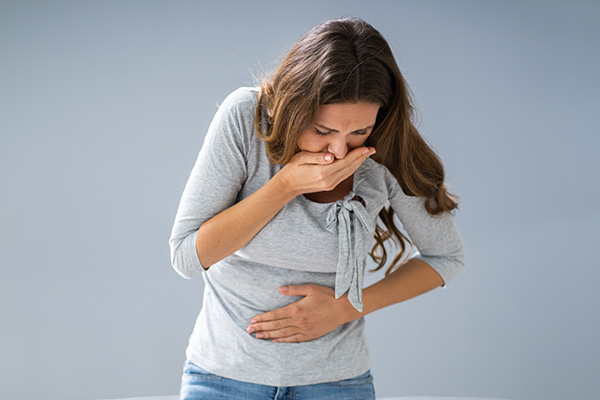

Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome is a complication of gonorrhea that occurs in women. It causes nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. (21)
Who are at higher risk of gonorrhea?
The following people are at risk of getting infected:
- People who do not practice safe sex (do not use condoms)
- People who have multiple sexual partners
- Pregnant women younger than 25 years of age
- People with a past history of STDs (22)
What is expedited partner therapy?
Expedited partner therapy (EPT) can help reduce the transmission and avoid re-infection of gonorrhea in patients. It involves the patient giving medication or the prescription to their sexual partners as well. (23)
Is there a vaccination for gonorrhea?
No, as of now, there is no vaccine for gonorrhea. However, scientists are testing multiple vaccines that may prove effective against gonorrhea, such as MeNB-4C. (24)(25)
Final Word
Like in everything, it is better to be safe rather than sorry. In the case of gonorrhea, prevention is better than cure. So, practice safe sex and avoid having more than one partner. Get yourself regularly screened if you have multiple partners to detect asymptomatic infections.
If you are diagnosed with gonorrhea, practice abstinence till you are completely cured, and also get your partner screened for gonorrhea. Exercise daily to build your immunity, eat a balanced diet, and keep yourself hydrated.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


