In this article:
The muscles of your body form the basis of your overall shape. The three main types of muscle include skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.

Muscle strength and muscle mass play a vital role in conducting routine day-to-day activities and exercise. Muscle influences protein metabolism and the energy balance throughout the body. (1)
Muscles also serve as the reservoir of glucose and amino acids. Muscle loss is associated with many pathological conditions, delayed recovery from illness, delayed wound healing, poor health, physical disability, poor quality of life, and increased mortality. (2)
The health status of your muscles is therefore an index of your overall health. It is therefore important to pay attention to muscle ailments and, if necessary, treat their underlying cause to maintain good health.
Read on to know more about the things your muscles are trying to tell you.
Things Your Muscles Are Trying to Tell You
Given below are some things your muscles are trying to tell you.
1. You need to increase water intake
In a study conducted in 2015, athletes training in a dehydrated state reported greater cellular and whole-body stress including an elevated body temperature, which led to a significant decrease in performance. (3) To improve performance, hydration and cooling strategies are recommended.
Another study recommended caution coupled with intermittent breaks and rehydration while exercising in hot humid climates to avoid skeletal muscle damage that can lead to delayed-onset muscle soreness (DOMS). (4)
An early indication of dehydration is muscle soreness and cramps. Hence, if you are experiencing sore muscles or muscle cramps, drink water in ample quantities to avoid dehydration.
2. You need a magnesium-rich diet

Magnesium is essential for muscular contraction. (5) It is needed for the transport of calcium across the skeletal muscle membrane during muscle contraction. Hence, a deficiency of magnesium can prove harmful to muscle health and affect muscle contraction. (5)
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include muscular spasms, cramps in the soles of the feet, leg cramps, and tremors.
Thus, if you experience frequent muscle cramps, get your magnesium levels checked and supplement your diet with magnesium-rich foods if necessary. Magnesium-rich foods include whole grains, nuts, green leafy vegetables, and fruits such as bananas and avocado.
If needed, consult your doctor and take magnesium supplements.
3. You need to increase protein intake
An inadequate intake of dietary protein leads to muscle breakdown to provide amino acids to allow for continued endogenous protein synthesis. (6) This, in turn, impacts adaptation to exercise, bone and calcium homeostasis, and fluid and electrolyte balance.
Symptoms of inadequate protein intake include muscle wasting, rapid loss of weight, and low immunity. An effective treatment is to increase the consumption of protein-rich foods such as lean meats.
4. Your body is lacking potassium
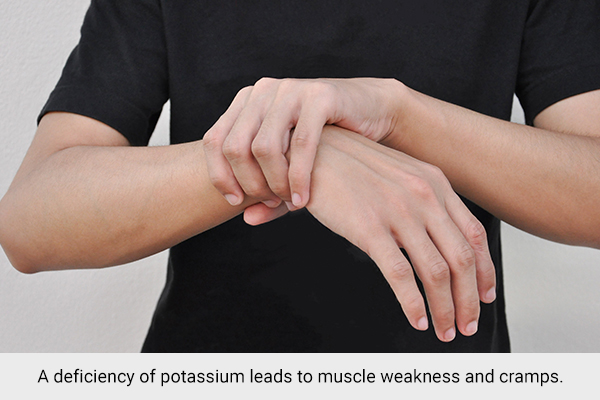
Potassium is required for the conduction of electrical impulses sent by the muscles. This ensures proper contraction of the muscles.
A deficiency of potassium leads to muscle weakness and cramps. A recent study conducted in 2020 showed that a higher dietary intake of potassium correlated with greater muscle mass in men, but in women, the effect was associated with overall energy intake. (7)
Foods rich in potassium such as spinach, bananas, and white beans can be consumed to replenish the body’s store of potassium.
5. You have to go easy on alcohol intake
Excessive alcohol intake can cause a lot of damage to the body, including damaging the muscles. It also impairs recovery after rigorous exercise.
A study conducted in 2014 on athletes showed that alcohol consumption reduces rates of myofibrillar protein synthesis (MPS) following a bout of concurrent exercise, even when co-ingested with protein. Thus, alcohol ingestion may impair recovery and adaptation to training and/or subsequent performance. (8)
Excessive drinking may also cause dehydration, which can lead to muscle soreness.
6. You need to take a break from cigarette smoking

Age-related loss of muscle mass is influenced by cigarette smoking. Cigarette smoking hampers muscle metabolism, increases oxidative stress, and promotes muscular atrophy (9)
Moreover, smoking affects blood circulation, and this, in turn, impairs the supply of nutrients to the musculoskeletal system, preventing the efficient functioning of muscles.
7. You are unable to concentrate and are experiencing mood disorders, so you’re lacking mind and body coordination
Skeletal muscles release a class of protein molecules called myokines, which transmit messages from the muscles to other organs including the brain.
Myokines are released into the bloodstream when your skeletal muscles contract. (10) One such myokine is the recently discovered protein irisin, which crosses the blood-brain barrier to initiate a series of reactions in the hippocampus, resulting in neuroprotection. (11)
A study conducted in 2019 provided evidence that increased muscular activity improves cognitive skills in old age and may even help to protect from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease. (12)
Prevention Tips by Experts
- Don’t exercise right after eating.
- Do some light stretching exercises before going to bed.
- Hydrate yourself after exercise; prefer potassium-rich beverages.
- Avoid consuming stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, ephedrine, and pseudoephedrine.
Try Doing the Runner’s Stretch
Perform the runner’s stretch, which is very useful.
How to do the runner’s stretch:
- Start in a lunge position with one leg bent forward at the knee while the other one extended straight behind.
- Place your hands on the wall to maintain body balance. Keep your heels firmly rooted in the ground.
- Throw your body weight on the front knee to bend it a little more until you feel a slight stretch along the back of the other leg. Increasing the space between your feet and bending the front knee further will result in a greater stretch, but don’t overdo it.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds and do 5 reps.
- Do the same steps on the other leg.
Most-Asked Questions
How does muscle affect metabolism?

Muscular activity such as walking, jogging, and other forms of exercise stimulates the metabolism of the body and induces “calorie burning.” This, in turn, burns up excess body fat, boosts immunity, improves energy levels in the body, and reduces stress.
How is the muscular system important for good health?
Muscles play a part in everything that you do. They control your heartbeat, breathing, and mobility, among others. Hence, keeping them healthy through regular exercise and eating healthy food is important.
What are the symptoms common to muscle disorders?
- Numbness or painful sensations
- Muscle weakness that can lead to twitching, cramps, and pains
- Difficulty maintaining balance
- Double vision
- Trouble breathing and swallowing
- Progressive muscle loss
Final Word
Muscles play an important role in maintaining your overall health and wellness. The health status of your muscles indicates a lot about the overall health of your body.
Hence, pay attention to any signs of muscle ailments and try to understand the underlying reason behind them.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


