In this article:
The recent COVID-19 pandemic saw a huge rise in the demand and use of hand sanitizers. Promoted as a tool to disinfect hands on the go, they aid in the fight against diseases that spread through touch.

Hand sanitizers are fairly inexpensive, easily available, and generally safe for use. Yes, you read it right – generally.
Before looking at the other side of the coin, get to know what a hand sanitizer actually is.
How Does a Hand Sanitizer Work?
Primarily containing a disinfecting agent, hand sanitizers are made in a water-based or alcohol-based formula, with alcohol being more common and preferred. The alcohol concentration (62%–95%) leads to changes in the structure of microorganisms, killing them and preventing disease. (1)
Risks of Hand Sanitizer Overuse
Though hand sanitizers seem like the one-stop solution for preventing the spread of disease, they should not replace handwashing with soap and water.
Medical experts have identified certain risks with overusing harsh chemical-based hand sanitizers on the skin.
1. Can compromise the skin barrier

Alcohol is a skin-drying agent and can lead to a loss of oil and water from the skin, making it rough and irritated. This can also cause cracking, which makes it easy for microorganisms to enter through the skin. (2)
2. Can lead to drug-resistant microbial strains
Drug-resistant microorganisms arise from the overuse of antibiotics and are a huge burden in healthcare. Such microorganisms stop responding to broad-spectrum and commonly prescribed antibiotics, increasing the duration and severity of illness.
And like antibiotic medication, hand sanitizers have also led to the rise of drug-resistant microbial strains. (2)
3. Can cause skin diseases
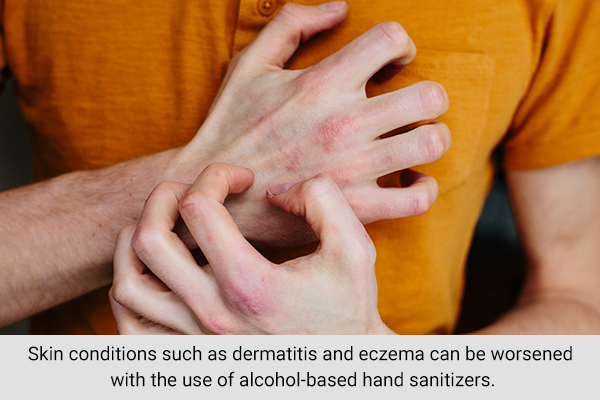
Skin conditions such as dermatitis and eczema can be worsened with the use of alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
In university students of Saudi Arabia, the use of hand sanitizers during the COVID-19 pandemic was associated with dermatitis, a skin condition characterized by irritation, rash, and/or blister formation. (3)
In another study in the Indian population, several patients had complaints of hand eczema after excessive use of hand sanitizers. (4)
4. May cause hormonal imbalances
Certain ingredients in alcohol-based sanitizers can have negative effects on the endocrine system, which includes the thyroid and parathyroid glands, which are responsible for maintaining metabolism, growth, and body temperature. (5)
5. Can cause damage to the eyes
Though sanitizer use will not directly impact the eyes, excessive use comes with the risk of contact with the eyes and mouth, especially in young children.
In a case study, a 5-year-old girl experienced severe eye burn after an alcohol-based sanitizer splashed in her eye. If this is not treated immediately, it may cause permanent damage to the eye. (6)
6. Can be poisonous if swallowed

Just like contact with eyes is damaging, accidental swallowing of alcohol-based hand sanitizers can cause blood clots to develop around the liver, damage the respiratory tract and nervous systems, and increase the chance of a heart attack. (2)
A doctor must be contacted immediately if you or your child accidentally swallowed hand sanitizer.
7. Cannot remove chemicals and heavy metals
Hand sanitizers can be effective in killing some disease-causing pathogens, but it is completely ineffective against some germs, chemicals such as pesticides, and heavy metals.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, washing your hands with soap and water is the only effective way to remove certain germs such as norovirus or clostridium. (7)
Studies have also reported an increased level of pesticides in the body of people who used hand sanitizers to clean their hands after exposure to pesticides. Therefore, make use of soap and water and avoid contact with your mouth and nose until you can wash your hands. (7)
How to Properly Use Hand Sanitizers

With schools resuming and COVID-19 still not being completely eradicated, many people, especially parents, rely on hand sanitizers to safeguard themselves and their children. Ensuring proper use of hand sanitizers can lead to the prevention of overuse and its side effects.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommend the following: (8)
- Using a sanitizer with a minimum of 60% alcohol.
- Place a small dollop of hand sanitizer on your palm and rub it properly covering all areas including between the fingers.
- Allow the hand sanitizer to dry, and do not wipe or wash your hands to allow proper disinfection.
- Use it after sneezing or after visiting a sick friend or relative.
- DO NOT use a hand sanitizer on dirty hands such as that covered in dirt and dust.
- DO NOT use a hand sanitizer before eating as this can lead to ingestion of the sanitizer. Instead, wash your hands with soap and water and dry them well.
Most-Asked Questions About Hand Sanitizers
Which hand sanitizer is the best?
Many brands of hand sanitizers are available. Choose one with a minimum concentration of 60% ethyl alcohol for it to be effective, and avoid overuse.
Are herbal hand sanitizers safe and effective?
Herbal hand sanitizers based on ancient and traditional remedies offer a safer solution as they are usually free of toxins and do not cause damage to the skin. Some studies have reported them to be effective in reducing microorganisms. However, more research is needed on this topic. (9)
Final Word
Hand sanitizers provide a modern and safe solution to reducing the risk of diseases. However, due to their strong alcohol content, they pose certain risks if not used properly.
There is a need to educate people, especially young children, about the risk of hand sanitizer overuse and how to prevent them.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


