In this article:
There are numerous reasons and underlying factors that may cause your fingers to experience swelling, but it is not necessarily an indication of a serious condition.

Typically, swelling occurs due to an accumulation of fluids or could be a manifestation of an inflammatory response. (1)
As stated by experts in the field, there are a plethora of factors that commonly lead to swollen fingers. (2) These may include, but are not limited to:
- Jammed finger
- Fluid buildup
- High salt intake
- Hormonal imbalance
- Infections
- Sprain
- Injury of finger
- Insect bite or sometimes sting
- Blood clot
Other than the above-mentioned reasons, various health issues, as shared by experts, can also cause your fingers to get swollen. These would include: (2)
When a finger becomes swollen, it can take a few days to return to its normal size. However, the inconvenience and pain caused by swollen fingers can hinder your daily activities, as you use your fingers extensively in your daily routine. (4)
To alleviate the discomfort associated with swollen fingers, there are several home remedies you can try.
Ways to Deal With Swollen Finger at Home
Below are some effective ways to treat swollen fingers.

1. Hot-cold water treatment of the finger
One effective method to reduce swelling in your fingers is to alternate between warm and cold water. You can do this by soaking your fingers in warm water for a few minutes and then switching to cold water for a minute or two. Repeating this process for about 15 minutes, at least twice a day, can help alleviate the swelling.
Also, washing and drying your swollen fingers regularly can help prevent infections from occurring. (5)
2. Massage the finger
To reduce swelling in your fingers, massaging them with warm olive oil can be an effective method. Simply use your opposite hand to gently massage your fingers for about five minutes, a few times a day. This can help improve blood circulation in the affected area, which may help reduce fluid buildup and alleviate swelling. (6)(7)
However, it’s important to be careful while massaging your fingers. If you experience any pain or discomfort while doing so, it’s best to avoid it. You don’t want to cause further harm or injury to your fingers.
3. Compressive wear
If you want to prevent fluid buildup and reduce swelling in your fingers, applying compression can be very helpful. You can easily find an elastic bandage at your local pharmacy for this purpose.
To use the bandage, wrap it around your wrist and palm, making sure to apply enough pressure to the affected area. This can help reduce pain and swelling. You can wear the bandage throughout the day and remove it at night. Just be sure not to wrap it too tightly, as this can impede blood flow. (8)
Remember, compression bandages can be a great way to help manage swelling, but it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional if the swelling persists or worsens.
4. Elevation of the affected finger
If you want to improve blood circulation to your fingers, one simple way is to elevate them above the level of your chest. This can help alleviate symptoms such as swelling, inflammation, and pain.
You can elevate your fingers at night by placing a pillow under your hand. During the day, you can place your hand on an armrest or other elevated surface. This will help increase blood flow and reduce discomfort in your fingers. (9)
5. Stay away from allergens
Swollen fingers can sometimes be caused by contact dermatitis, which is an allergic reaction to something that comes in contact with the skin, such as soaps, fragrances, cosmetics, or detergents.
If you suspect that an allergen or an irritant is the cause of your swollen fingers, you should try to identify the source and avoid it in the future.
To reduce irritation, you can wash your hands with cool water and a gentle, fragrance-free soap. It typically takes two to three weeks for swelling caused by contact dermatitis to go away. (2)
Herbal Remedies for Swollen Fingers Management
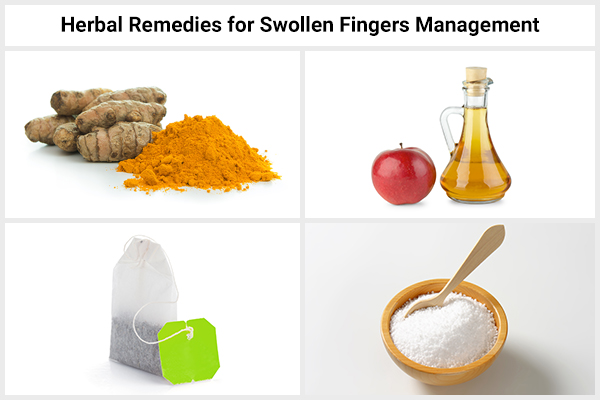
Here are some home remedies which may help to reduce and treat swollen fingers:
1. Apply turmeric topically
If you’re experiencing swelling in your fingers due to an inflammatory response, turmeric can be a natural way to help alleviate the symptoms.
Turmeric contains a chemical compound called curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. This can be particularly helpful in cases of arthritis, sprains, and other similar conditions.
To use turmeric, you can make a paste with turmeric powder and olive oil, and then apply it to the affected fingers. This can help reduce swelling and inflammation, and may also help relieve pain. (10)
2. Use tea bags
Tea bags can be a simple and natural way to help alleviate symptoms associated with swollen fingers.
Tea bags are packed with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, as well as a chemical compound called tannin, which can help manage swelling and fluid buildup.
To use tea bags as a remedy, simply dip them in water and then refrigerate them for a few minutes. Once they’re cool, apply the cold tea bags to the affected fingers for a few minutes. (11)
This can help reduce swelling and inflammation, and may also help relieve any discomfort you’re experiencing. Remember to use a fresh tea bag each time you apply it.
3. Try using apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is beneficial for swollen fingers as it contains high levels of potassium that can reduce the buildup of excess fluid causing swelling. Additionally, it helps to maintain the proper pH level in the body, which can also help to reduce swelling.
To use apple cider vinegar for swollen fingers, you can soak a cloth in apple cider vinegar and wrap it around the affected finger for a few minutes. This can be repeated a few times a day to experience relief. (12)
4. Use Epsom salt
Epsom salt is a natural remedy that can help to reduce swelling. You can soak the affected body part in a mixture of warm water and Epsom salt, which contains minerals that help fight inflammation and provide relief. This is an easy and effective way to soothe swollen areas and feel better. (13)
Diet and Exercise to Help Deal With Swollen Fingers
Diet and exercise also play an important role in managing swollen fingers. Here are some lifestyle changes to deal with swollen fingers:
1. Controlling salt intake

Eating too much salt can sometimes cause your fingers to swell up. (2)
When you eat salt, your body tends to hold on to extra fluid, which can lead to swelling and buildup. To reduce your chances of swelling, it’s a good idea to limit the amount of salt you eat.
Instead of adding lots of salt to your food, try using other seasonings to add flavor. And it’s best to avoid packaged foods, which can be high in sodium.
By being mindful of your sodium intake and making some simple changes to your diet, you may be able to reduce your risk of swollen fingers and other related health issues. (14)
2. Exercising
If your swollen fingers are due to poor blood circulation, one way to help reduce the swelling is by exercising your fingers.
Exercise can increase blood flow to the affected area and help to drain excess fluid. One simple exercise you can do is finger flexing. Start by stretching out your fingers as far as you can, then slowly make a fist and release. Repeat this exercise a few times a day to help improve circulation and reduce swelling.
By incorporating finger exercises into your daily routine, you may be able to manage your swollen fingers and improve your overall hand health. (15)
What Are the Medications to Treat a Swollen Finger?
Here are some medications to treat a swollen finger:
1. NSAIDs
If you have swelling due to arthritis, taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications like Ibuprofen can help in reducing the inflammation and provide relief. NSAIDs are also available in topical ointment form for use on your hand. (2)
Make sure to take these medications as directed by your doctor, and don’t exceed the recommended dosage.
Additionally, it’s always a good idea to discuss the use of any medication with your doctor, as they can advise you on the best course of action for your specific condition.
2. Antibiotics
If you have a swollen finger due to an infection, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. You can either call your hand surgeon or go to the emergency room for an evaluation. Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and, in some cases, surgery may be needed to remove the infected tissue. (2)
Note: Don’t delay seeking treatment as infections can quickly worsen and lead to serious complications.
What Not to Do With Swollen Fingers?
If your fingers are swollen, there are certain things you should avoid doing.
- First, before exercising, it is important to loosen any jewelry or accessories, such as rings and watch bands, that could impede blood flow to your fingers.
- Second, try not to stay in the same position for too long as this can slow down the healing process. Instead, try to move the fingers around to improve blood circulation.
- It is also important to treat any underlying conditions that may be causing the swelling. If you are taking steroids or medication for hypertension, talk to your doctor about possible alternatives. (2)
What Type of Food is Good for Swollen Fingers?
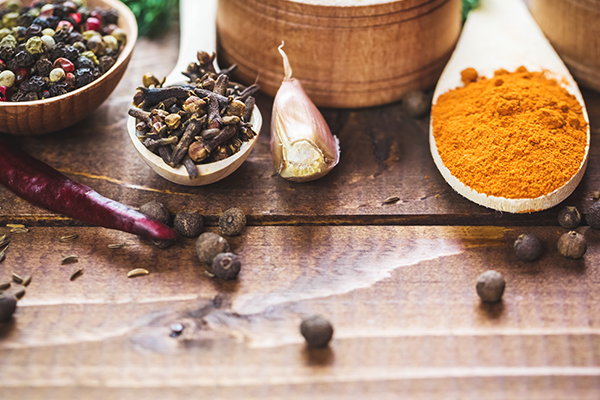

Including foods that are rich in anti-inflammatory compounds in your diet is a good idea if you have swollen fingers. These include: (16)
- Ginger
- Garlic
- Cinnamon
- Cloves
- Peppers
- Dark chocolate
- Fish
- Tomatoes
- Leafy greens
- Nuts
- Cherries
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor for your swollen fingers:
- If you have diabetes and both your hand and arm are swollen.
- If the swelling becomes severe, very painful, or starts suddenly.
- If you have swelling in only one hand without an obvious cause.
- If the swollen area becomes red or you feel a burning sensation in your fingers. Additionally, if you have a fever or chills.
- If you experience shortness of breath.
Final Word
Swollen fingers can be a minor inconvenience or an indication of a serious condition. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of the swelling and seek medical attention if needed. However, there are several home remedies available that can help alleviate discomfort associated with swollen fingers.
Hot-cold water treatment, massage, compression bandages, elevation, avoiding allergens, and using herbal remedies such as turmeric, tea bags, and apple cider vinegar are all effective ways to manage swollen fingers.
It’s important to remember that while these remedies can help alleviate symptoms, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional if the swelling persists or worsens.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


