In this article:
Hyperthyroidism refers to excessive production of thyroid hormone in the body due to an overactive thyroid gland. The treatment for hyperthyroidism depends on the type, cause, and severity of the condition and your age and medical conditions.
Introducing changes in your diet and lifestyle may help enhance the efficacy of your medications and support the health of your thyroid.
Vitamins and Minerals for Hyperthyroidism
The following vitamins and minerals may be associated with the management of hyperthyroidism or its symptoms. Therefore, modifying your diet to include these nutrients can help.
Note: Supplements for the following minerals and nutrients can also be taken. However, they should only be used with your doctor’s prescription for a diagnosed deficiency. Overuse of supplements can have detrimental effects on your health.
1. Selenium

Selenium may help balance thyroid function. A study showed that taking a selenium supplement along with medical therapy for Graves’ disease for 6 months had a positive effect on response to the medication. (1)(2)
Moreover, selenium is found to play a role in preventing thyroid disease. (3) Selenium-rich foods include eggs, fish, chicken, turkey, Brazil nuts, and beans.
2. Vitamin D and calcium
Calcium and vitamin D levels need to be optimized due to the detrimental effects of hyperthyroidism on the bones. Optimal replacement is necessary if deficiency is found. (4)
A deficiency of vitamin D increases the risk of Graves’ disease and autoimmune thyroid disorders. (5)(6) Include foods such as tofu, cheese, milk, green leafy vegetables, sardines, mushrooms, and almonds in your diet.
3. L-carnitine
Oral intake of carnitine is seen to help reverse and prevent hyperthyroid symptoms to some extent. (7)(8) It may also help manage Graves’ disease without the support of anti-thyroid drugs. (9)
Consume foods such as avocado, dairy products, chicken, and red meat to increase your carnitine intake.
Alternative Therapies for Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is associated with various mental health conditions such as ADHD, bipolar disorder, depression, adjustment disorder, anxiety, and suicidality. (10)
The following alternative techniques for relaxation can help prevent and manage these mental health conditions:
1. Yoga
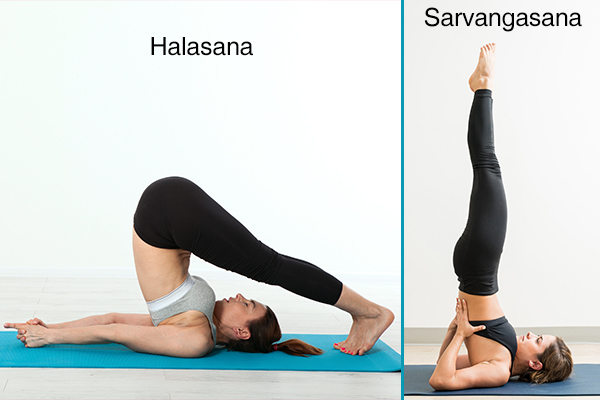

Performing yoga asanas, such as Halasana and Sarvangasana, helps stimulate the arteries attached to the thyroid gland. This induces a state of homeostasis that helps alleviate the associated symptoms. (11)(12)
2. Music therapy
Progressive music relaxation involves contracting and relaxing different muscle groups to relieve tension and anxiety. This helps reduce stress and also induces sleep, helping you avoid sleep problems.
3. Mindful meditation
Mindful meditation aims at focusing your attention on the present. By noticing your surroundings and accepting them, you become mindful of the situation without trying to control them.
Self-Care and Lifestyle Tips
The following tips can help manage your hyperthyroidism in the long run:
1. Keep a check on your iodine intake

Excessive intake of iodine is often associated with an increased risk of thyroid problems.
If you have already been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, it is recommended that you keep a close tab on the amount of iodine you consume daily, and do not add iodine to your diet or take it in supplement form.
You should neither overindulge on nor starve yourself of iodine-rich foods, but adjust your intake to meet the daily requirement without surpassing the upper limit of the stipulated dietary allowance. (13)(14)
2. Implement dietary changes
Patients with hyperthyroidism have increased markers of oxidative stress and many have lost significant weight.
A plant based diet rich in fruits and vegetables may help in reducing the risk of diseases related to oxidative stress. (15)(16) In particular, more protein may be necessary if there has been a lot of weight loss and muscle wasting. Consultation with a registered dietitian may be beneficial.
3. Take OTCs for swollen eyes
Graves’ disease often causes swelling in the eyes due to the receding upper eyelids. While extreme cases require surgery, mild cases can be managed by wearing sunglasses and using artificial tears.
You may also consult your doctor for corticosteroids or hydrocortisone for relief.
Most-Asked Questions About Hyperthyroidism
Does hyperthyroidism necessarily lead to weight loss?
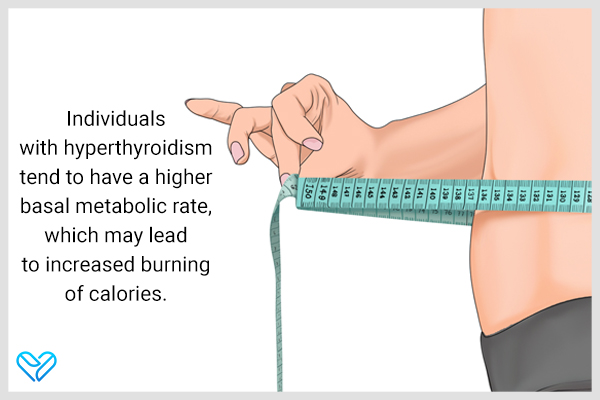
Individuals with hyperthyroidism tend to have a higher basal metabolic rate, which may lead to increased burning of calories.
A rapid calorie loss may promote unintentional weight loss, a typical symptom of hyperthyroidism. However, some patients with hyperthyroidism may gain weight rather than lose it.
Is lemon balm tea effective in managing hyperthyroidism?
It has been shown that lemon balm prevents antibody attachment to thyroid cells, as seen in Grave’s disease. However, there is a need for clinical trials to establish this claim. (17) However, a study showed that a natural health supplement containing lemon balm induced hyperthyroidism in a woman. (18)
Lemon balm also has various side effects, including headache, nausea, fever, abdominal pain, dizziness, painful urination, and wheezing.
Is bugleweed supplementation good for managing hyperthyroidism?
Bugleweed pill or powder has been used for the treatment of milk hyperthyroidism. However, there aren’t enough conclusive studies that establish its efficacy. (19) Therefore, it is best to avoid bugleweed supplementation.
Final Word
It is vital to treat hyperthyroidism at the earliest to avoid other health complications such as osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases. Even during treatment, regular monitoring of hormone levels is necessary to prevent a state of hypothyroidism.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY



