In this article:
Goiter is a condition in which there is an abnormal growth of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is the second major gland in the body and is located in the neck region. It secretes the thyroid hormone, which regulates many body functions such as oxygen intake, growth, and metabolism. (1)
Hence, any perturbation of thyroid function affects a number of physiological processes.
A hyperactive thyroid is a condition known as hyperthyroidism and an underactive thyroid is a condition known as hypothyroidism. Both these disorders affect 1.6 billion people in more than 100 countries around the world. (2)
Goiter often occurs along with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. It is not representative of a single medical condition but can stem from many different underlying medical issues such as autoimmune disorders.
Exogenous environmental factors such as lack of iodine in the water and food as well as physiological factors such as the onset of puberty, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and menopause in women can all play a role in goiter formation. (3)
Causes, Symptoms, and Types of Goiter
World over, the most common cause of goiter is iodine deficiency. This can be due to endemic factors such as iodine-deficient soil or water.
Other factors that predispose you to goiter are environmental such as pesticides, fungicides, and insecticides which interfere with thyroid function. (3)
Goiter is an overgrowth or protrusion at the front base of the neck that occurs when the underlying entire thyroid gland becomes enlarged or develops one or more nodules. It can develop in the shape of a tiny bump, multiple nodules, or general swelling on one or both sides of the throat.
This overgrowth is usually accompanied by the following symptoms: (3)(1)
- Excessive fatigue
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Increased sensitivity to heat and cold
- Tremors
- Muscle weakness
- Insomnia (3)
- Hoarseness of voice
- Tightness in the throat
- Dizziness when elevating your arms
- Swollen veins in the neck
- Coughing
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
Toxic goiter with hyperthyroidism may present the following symptoms:
- Sweating
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Rapid heartbeat or pulse
- Shakiness or hand tremors
- Weight loss despite an increased appetite
- High blood pressure
- Hot flashes
- Nervousness
- Muscle weakness
If you have hypothyroidism, you could notice:
- Skin dryness
- Constant fatigue
- Unexplained weight gain
- Constipation
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Slowed physical and mental functions
- Depression
- Slow heart rate
- Feeling cold for no reason
- Tingling or numbness in your hands
Goiters can be broadly classified into the following categories depending upon the cause of the swelling in the thyroid gland: (1)
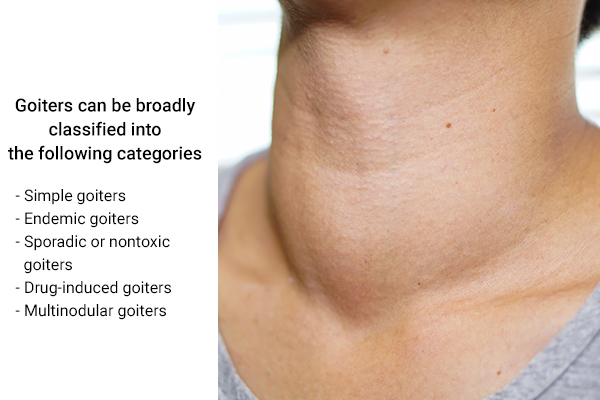
- Simple goiters are typically associated with hypothyroidism or the inability of the thyroid gland to produce enough hormones. The thyroid starts growing in size to compensate for this deficiency and protrudes out of the neck in the form of a goiter.
- Endemic goiters or colloid goiters develop when you don’t get enough iodine through your diet. The body uses iodine to produce thyroid hormones. This is perhaps the most common form of goiter, but it is not prevalent in areas where iodine is added to table salt, such as in India (Jammu and Kashmir).
- Sporadic or nontoxic goiters are generally idiopathic, which means they don’t have a known cause.
- Drug-induced goiters develop due to prolonged use of certain medications such as lithium, which is prescribed for mood disorders, and amiodarone, which is prescribed for an irregular heartbeat.
- Multinodular goiters occur due to the development of lumps or nodules inside the thyroid gland.
Treatment Modalities for Goiter
Goiters can usually go without treatment if they are small and occur without any symptoms or abnormalities in your thyroid hormone levels. But treatment is necessary if there is an excess or deficiency of thyroid hormones in the blood along with goiter formation.
Conventional treatment involves medication to either increase or decrease thyroid hormone production. It involves medication to either increase or decrease thyroid hormone production. These treatments include the use of radioactive iodine and thyroid-suppressing drugs such as levothyroxine and thionamides. (1)
Hence, home remedies are much sought after.
Diagnosing Goiter
Goiter is usually detected by a routine physical examination wherein your healthcare provider may detect an enlargement of your thyroid by just touching your neck.
Additional tests to confirm the initial diagnosis need to be done, and these are:
- Thyroid function test to measure the level of thyroid hormone in the blood
- Antibody test to check for autoimmune disorders
- Ultrasound (1) to determine the size of the enlarged thyroid gland and look for the presence of nodules
- Fine-needle aspiration biopsy if the size of the nodule is 1 cm or larger (1)
- A thyroid scan to check the size and functioning of your thyroid gland
- A CT scan or MRI if your goiter becomes quite large or spreads to your chest area (1)
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies to Manage Goiter
Iodine deficiency has emerged as the leading cause of goiter formation. So, if you wish to avoid or control this problem, the first thing you need to do is to meet the recommended daily intake of iodine, which is 150 micrograms.
There are nearly 250 micrograms of iodine in a teaspoon of iodized salt. (4)
Your body derives iodine from the foods you eat. Here are some iodine-rich foods that you should consider adding to your diet:
- Saltwater fish and shellfish
- Seaweed
- Dairy products
- Soy products (4)
In addition, you can try the following home remedies.
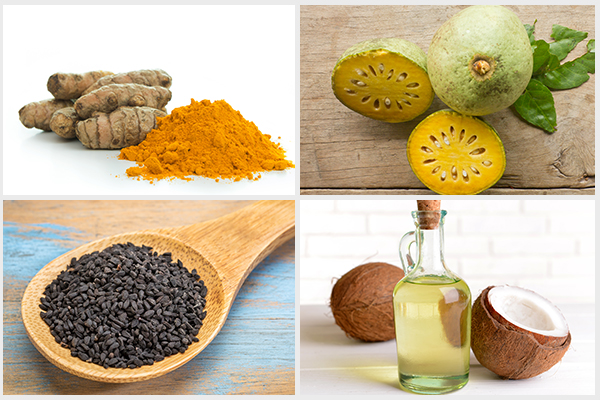
1. Turmeric
The active ingredient of turmeric (Curcuma longa) is curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties. Administration of curcumin has been shown to cause a reduction in the size of thyroid nodules. (5)
2. Stone apple or bael
Stone apple is an herb traditionally used in Indian medicine and has antioxidant properties. It causes a reduction in the symptoms of hyperthyroidism. In fact, it was shown to be superior to conventional treatments. (6)
3. Black cumin
Black cumin (Nigella sativa) is one of the easiest remedies available since it is used as a spice in regular cooking. Black cumin improves thyroid function and ameliorates the metabolic disorders associated with goiter. (7)

4. Haizaoyuhu decoction
Haizaoyuhu is a traditional Chinese herbal medicine concoction consisting of kelp (a species of seaweed native to East Asia and Southeast Asia), a type of lily, mandarin orange, ginseng, tangerine peel, licorice root, and some other herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine. (8)
The Chinese have been using it to treat goiter for 500 years. This formulation is iodine-rich and is hence considered as the gold standard for the treatment of goiter.
5. Alba
An herbal preparation of alba (the root extract of Potentilla alba, which is native to central and eastern Europe) was used to effectively treat goiter. It effectively reduced the volume of goiter in the Ukrainian population. (9)
6. Coconut oil
The medium-chain fatty acids in coconut oil help in modulating thyroid function. Virgin coconut oil along with soy oil and moringa seed oil has been shown to be very effective in treating thyroid disorders. (10)
7. Ginger
Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties, and this is useful in reducing the swelling associated with goiter. It can be easily taken as ginger tea. (11)
8. Ashwagandha
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an herb that has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce the swelling in goiter. (12)
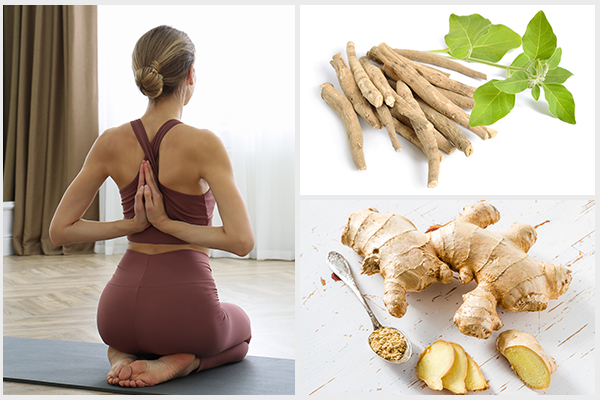

9. Yoga
Yogic postures (asanas) such as vajrasana, thadasana, shavasana, and bhujangasana and yogic breathing exercises (pranayama) such as anulom vilom, sheetali, and brahmari may help regularize thyroid function according to a recent report. (13)
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you experience any of the aforementioned symptoms along with an abnormal protrusion or swelling on the neck.
The goiter itself may or may not require treatment, but it is usually accompanied by hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, which needs to be managed to ensure proper body function and overall health.
Goiters tend to grow at a slow pace, but they can become large enough to trigger some serious problems. If the thyroid gland swells too much, it starts pressing on the jugular vein, the windpipe, the food pipe, and the nerve that runs through the larynx, causing labored breathing, difficulty swallowing, neck pain, dizziness, insomnia, and voice changes, among other complications.
Such goiters need to be medically treated and even surgically removed.
Most-Asked Questions About Goiter
What does a goiter look like?
A goiter is an irregular growth of the thyroid gland.
What is the most common cause of goiter?
Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of goiter.
What happens if goiter is left untreated?
An untreated case of goiter can result in other health problems over time, such as obesity, joint pain, heart disease, and infertility.
Moreover, considerable research from all over the world has shown that iron deficiency, which is a prime culprit behind goiter formation, can significantly hamper early brain development, cognition, and learning abilities in children.
How does the thyroid hormone affect the body?
Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) play a crucial role in regulating the following physiological functions that affect every cell and organ in the body:
- Metabolism, which is the rate at which your body converts food into energy or calories and then burns those calories. The metabolic rate, in turn, affects your ability to lose or gain weight.
- Heart rate
- Body temperature
- The movement of food through the digestive tract
- Brain development
- Muscle contraction
- Cell renewal (replacement of old, dead, or damaged cells with new healthy ones), which is essential for maintaining skin and bone health
Final Word
The home remedies given above are no doubt effective in treating goiter. However, if the symptoms persist, do consult a doctor.
Thyroid problems including goiter, if left untreated, could lead to a number of different complications such as bulging eyes, blurred vision, and even loss of vision.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


