In this article:
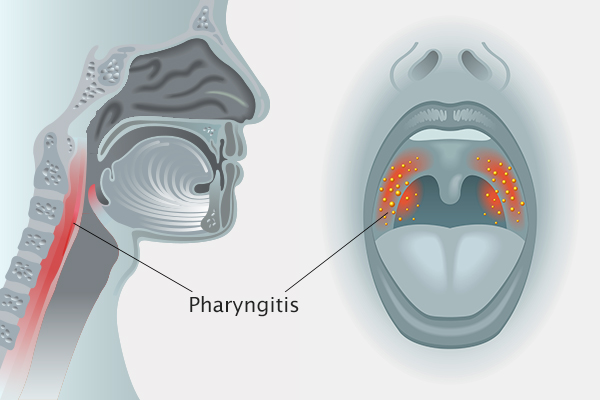
The pharynx is part of the upper aerodigestive tract or system, closely connected to the airway. Pharyngitis refers to inflammation of the mucosa (lining) of the pharynx or throat. It is generally caused by an infection, but not limited to it.

What Causes Pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis has various causes, including chemical, environmental, and infectious agents.
1. Infectious causes
Bacteria, viruses, and, to a lesser degree, fungi all live in the upper mucosa of the pharynx. It is when an opportunistic level of one of these microorganisms increases that infectious pharyngitis occurs.
- Bacterial: The symptoms usually have a rapid onset, often within hours to a day. Pain, fever, and swelling can be quite severe, along with swallowing concerns. A “strep” throat is a common example.
- Viral: The symptoms have a far slower onset, often preceded by a slow awareness of not feeling well, called a viral prodrome. Again, pain, fever, swelling, and swallowing difficulties are present. Mononucleosis is a common example. It is possible that a viral infection can bring on a bacterial suprainfection, thus giving the symptoms of a more acute process.
- Fungal: This is most often seen in immunocompromised individuals, such as those on chemotherapy or with diabetes, chronic illnesses, or diseases such as HIV, where the person’s immune system is not working properly. (1)
2. Non-infectious causes
These include extrinsic environmental factors such as:
Some intrinsic factors can also contribute to the development of pharyngitis:
- GERD/acid enzyme reflux, often with a feeling of fullness when swallowing, a new awareness of swallowing, frequent throat clearing, and mild voice change
- Swallowing disorders such as achalasia and Barrett’s esophagus
Common Symptoms of Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis generally manifests the following symptoms:
- Throat pain
- Inflammation
- Drooling or inability to handle the reflexive swallowing of saliva
- Difficulty breathing and/or speaking
- Fever
- Infection
Medical Treatment for Pharyngitis
If caused by an infectious agent, suitable antibacterial, antiviral, or antifungal medicine is required to treat pharyngitis.
For non-infectious causes, treatment is required to stop the inflammation caused by the underlying cause. This is accompanied by either the removal of the agent and/or treatment of the underlying disease.
Often, anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen are used in both infectious and non-infectious pharyngitis. In some cases, steroids are used if the mucosal swelling in the pharynx is severe.
Can Any Allergies Lead to Pharyngitis?
Yes. The allergic response is an anti-inflammatory action and, thus, can cause swelling and pain in the throat leading to swallowing difficulties.
Dietary Changes During Pharyngitis

Since the inflammation can cause difficulties in swallowing food, it is suggested to limit your diet to soft foods and liquids. Solids can put undue stress on the pharynx and aggravate the pain.
Once the symptoms improve, you can gradually add solid hard foods to your diet.
However, if the pharyngitis is caused by GERD, which presents with chronic symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor for long-term diet changes that will help manage the disease.
Recovery Period for Pharyngitis
This is entirely dependent upon the underlying cause of the inflammation.
- For the most part, pharyngitis caused by bacterial infections lasts for a few days, while that caused by a viral infection lasts for a week or more.
- Since fungal-caused pharyngitis is common in immunocompromised patients, the problem can be long-lasting in such cases.
- The resolution of pharyngitis caused by non-infectious sources depends on the removal of the causative agent or chemical or the treatment of the underlying disease.
Benefits of a Salt Water Gargle to Treat Pharyngitis

Warm or cold salt water is a hyperosmotic solution (denser than water) that removes water from infectious bacteria, killing them. These gargles also line the mucosa with a layer of salt that blocks infectious and environmental agents from affecting the mucosal lining of the pharynx. (3)
Apple Cider Vinegar and Honey for Treating Pharyngitis?
Vinegar, being an acidic fluid, is helpful as long as the harshness is not painful. Infectious bacteria and fungi do not do well in an acidic environment.
Honey again is a hyperosmolar solution such as salt water, which can help prevent and treat infections.
Use a Humidifier to Ease Pharyngitis Symptoms
A humidifier helps keep the mucous membrane of the pharynx moist, maintaining the fluid barrier that protects the mucosal lining. Therefore, a humidifier can help improve the symptoms. This is very important in a heated or air-conditioned room.
Potential Complications of Untreated Pharyngitis
This is dependent upon the cause, but swallowing problems can continue until the pharynx mucosa is healed. Rarely, pharyngitis can develop into a retropharyngeal abscess, which is a serious issue requiring rapid diagnosis and treatment.
Can Pharyngitis Turn Into Pneumonia?

Yes. Just as the bacteria, viruses, and fungi can be coughed out onto others if you do not wear a mask, they can be inhaled into the deeper airway – the trachea and lungs – and cause pneumonia.
The causative agents can include non-infectious elements, such as inhaled chemicals or stomach acid.
Is Pharyngitis an STD?
Yes! Some causes of pharyngitis can be caused by bacterial and viral STDs.
Is Pharyngitis Contagious?
Infectious causes of a disease can be contagious, as we are now seeing in COVID-19! Wearing a mask whenever one feels ill is crucial to prevent contagion to family, friends, coworkers, and all people.
Difference Between Laryngitis and Pharyngitis
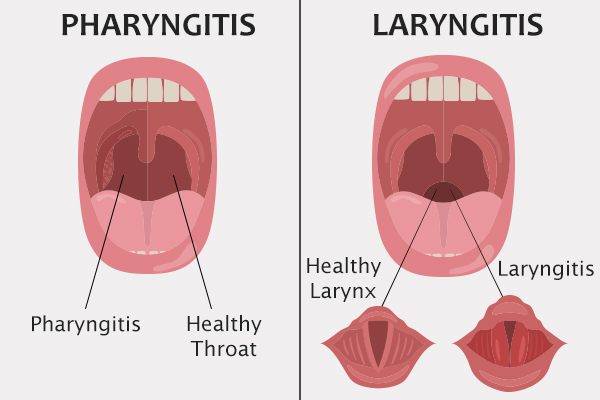
Pharyngitis is the inflammation of the mucosa of the pharynx/throat, which is part of the digestive system.
On the other hand, laryngitis is the inflammation of the larynx/voice box, which is part of the airway system. Though these are different illnesses, they occur in the same area of the body and can often coexist or become sequential.
Final Word
Generally, pharyngitis is a mild problem that doesn’t have any long-lasting complications. However, when caused by severe diseases such as strep, rheumatic fever, and kidney diseases, rare complications may occur.
It is suggested to gargle with salt water and consume soft foods to help manage the inflammation. Consult your doctor if the symptoms persist.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


