In this article:
The human skull contains four pairs of interconnected air-filled cavities around the nose, which are referred to as sinuses.
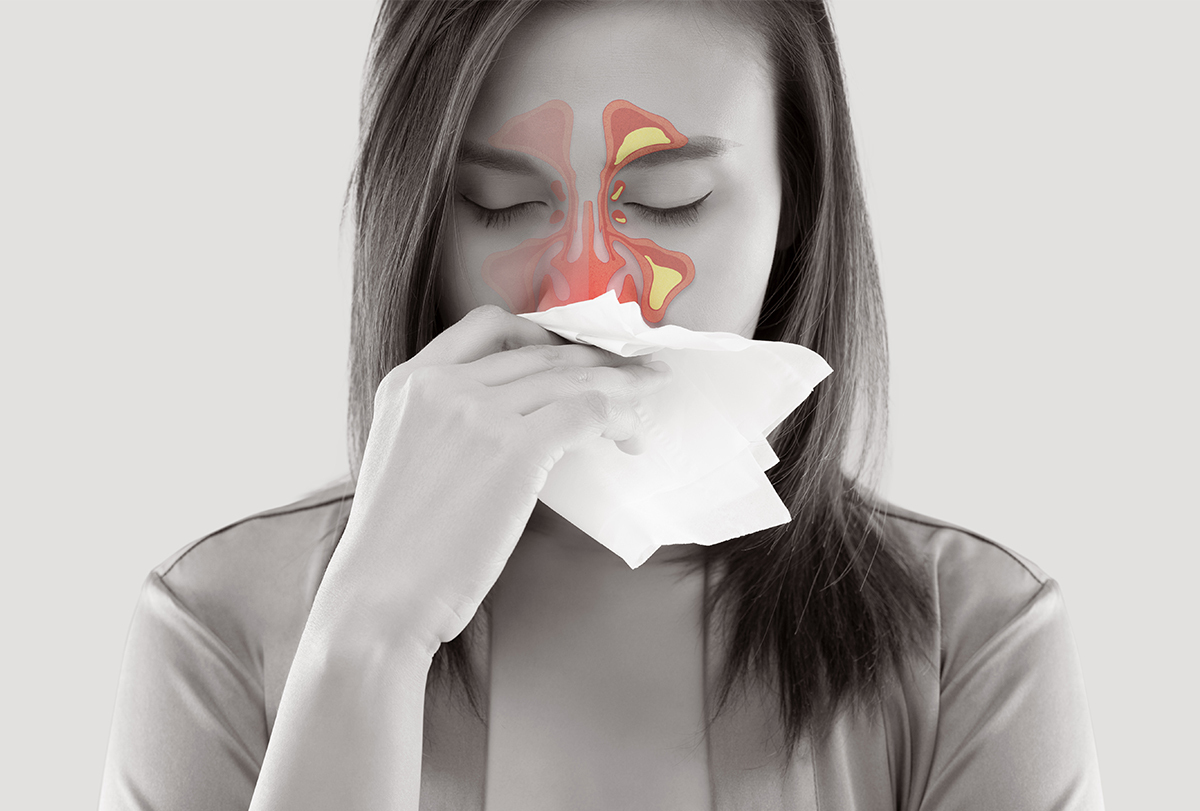

The walls of these hollow cavities contain thin mucus-secreting membranes and are lined with tiny hair-like outgrowths called cilia. The cilia push the mucus produced within the sinuses toward small openings that lead to the nose so that it can be drained out.
When the sinus tissue becomes inflamed due to an infection or allergy, the cilia are unable to function properly. As a result, the fluid discharge is trapped within the sinus cavity, making it a breeding ground for germs, resulting in an infection.
What Is Sinusitis?
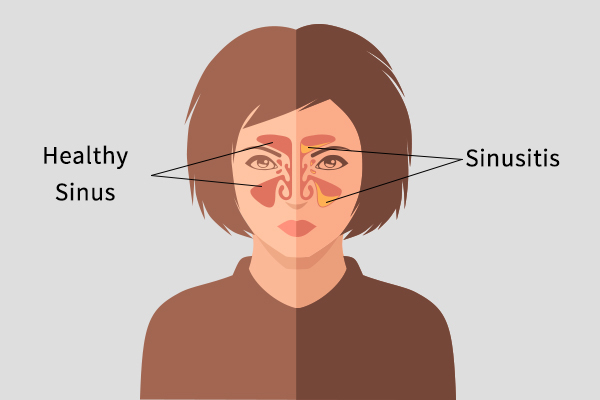
Inflammation of the sinuses that blocks the drainage of mucus into the nose is called sinusitis. (1) It is usually caused by a bacterial infection, but the entry of certain viral and fungal pathogens in the respiratory tract can also trigger swelling of the sinus tissue.
Inflammation of the sinuses can also occur as an allergic response, which is referred to as “allergic sinusitis.” (1) Acute sinusitis is an infection of the sinuses that lasts for 3 weeks or less. Chronic sinusitis is a sinus infection/inflammation that persists for more than 3 months.
A sinus infection that lasts between 3 weeks and 3 months is referred to as subacute sinusitis.
Medical Treatment for Sinusitis
Most sinus infections, whether bacterial or viral, resolve on their own unless there are predisposing factors. In fact, 70% of bacterial sinusitis cases resolve on their own. (2)
1. Antibiotics
The following are the guidelines for when to consider using antibiotics for an uncomplicated acute sinus infection:
- Severe symptoms, such as headaches and high fever.
- Symptoms getting worse or not better by 10 days.
- The patient has a history of allergies and sinus surgery or is prone to sinus infections.
- The patient may be flying or have worsening symptoms after a flight.
Chronic sinusitis requires medical treatment of the underlying factors such as allergies, 3–4 weeks of antibiotics, a trial of nasal steroids, and a referral to an ENT specialist.
A CT scan is often done to help understand the anatomy of the sinuses and confirm the diagnosis of chronic sinusitis. It usually occurs as a result of dental causes (3) or nasal polyps. (4)
2. Surgery
Sinus surgery is helpful in a majority of patients who suffer from chronic sinusitis and have failed medical management. There is an 80%–90% quality of life improvement in such patients.
It should be noted that smoking is deleterious to the lining of the sinuses and can lead to higher rates of infections and failure of surgery in such patients. (5) Some ENT surgeons do not recommend surgery in a patient who has not given up smoking.
Tips to Manage a Sinus Infection

Here are some tips to unblock the sinuses and help manage the symptoms associated with sinusitis:
- Like any illness, rest, plenty of fluids, and avoiding alcohol and cigarette smoke are important to recover quickly.
- For acute sinusitis not requiring any antibiotics or not leading to complications, over-the-counter medications such as decongestants, antihistamines, and saline sprays or washes can be helpful.
- Steam inhalation is also a natural and helpful way to help drain out the mucus and unblock the sinuses.
- Cold foods can temporarily worsen swollen nasal tissues and the accompanying postnasal drainage. Conversely, warm foods and soups can feel soothing and comforting.
- Flying with a sinus infection can make your condition worse and can also lead to ear pain/Eustachian tube dysfunction. (6)
- If flying with an infection, make sure to drink lots of fluids. Using nasal decongestants can help, and the physician should have a lower threshold to prescribe antibiotics. Nasal decongestants such as oxymetazoline and phenylephrine can help to decrease nasal congestion and aid in the unblocking of sinuses. However, they should not be used for more than 3–5 days in a row as they can lead to rebound swelling.
- Nasal allergies or exposure to irritants can lead to more sinus infections. Using sinus rinses (such as a neti pot) is very helpful in reducing the number of sinus infections. This is also true for those who are suffering from chronic sinusitis.
- In severe cases that may necessitate the use of antibiotics, the patient may be given a preliminary dose of oral steroids to decrease the swelling of the sinus lining. This allows the antibiotics given thereafter to pass through more easily and also help unblock the narrow drainage pathways of the sinuses.
- When severe complications such as abscess are seen, urgent surgery to unblock the sinuses and drain the infection is needed in addition to the medical treatment.
Bacterial vs. Viral Sinus Infection
The notion that having green mucus means bacterial infection is not true. The most common way of diagnosing bacterial sinusitis versus a viral one is the timeline, as most sinus infections start as viral infections.
Often, bacterial superinfections are contracted, and if the sinus symptoms get worse after the first few days or if the symptoms are not better in 7–10 days, antibiotics are considered. The exceptions for starting antibiotics sooner are severe sinus infections, complications, and a history of recurrent sinusitis.
Sinusitis in Children
Children are more prone to nasal congestion and drainage (which is hard to distinguish from sinusitis) as they get more colds and other respiratory problems. Also, little children have sinuses that are not fully developed and are more prone to having inflammation/infection of the nose and adenoids. (7)
Chronic cough from postnasal drainage, bad breath, and nasal congestion are clues to chronic sinusitis as young kids are not able to provide a history of facial pressure, etc. Acid reflux can also contribute to chronic sinusitis in younger children.
Why Do the Symptoms of Sinusitis Get Worse During the Night?
The symptoms of sinusitis get worse at night due to the following reasons:
- Lying down causes poorer drainage of the swollen tissues of the nose and sinuses along with the accumulation of mucus, which clears more easily when you are upright and awake.
- When the nose is blocked due to sickness, the affected individual mouth breathes, causing a dry and sore throat on waking up. This also causes a bad smell in the mouth.
- Often, medicine is taken during the day every few hours, which may not be done when asleep. Hence, the affected individual may wake up feeling worse.
Can Eye Strain Worsen or Bring on a Sinus Headache?
A sinus headache is associated with pressure in the head and face, usually experienced during a bout of acute sinusitis. This is very often confused with more common causes of headaches, such as migraines.
Eye strain does not lead to a “true” sinus headache as such headache is caused by acute inflammation and blockage of the sinus cavities.
Complications of an Untreated Sinus Infection

Most sinus infections will resolve on their own, as mentioned above. However, acute sinus infections can lead to serious complications in immunocompromised individuals or in a severe sinus infection from more virulent forms of bacteria.
Here are some of the complications:
- The infection can spread to the eyes, resulting in cellulitis. It is characterized by eye swelling or abscess (a collection of pus).
- The infection can spread to the brain, which can present as meningitis (8) (infection of the lining of the brain) or abscess.
- The infection can spread locally. Pott’s puffy tumor (9) is a swelling on the forehead when the frontal sinus is blocked, leading to a local infection of the bone.
- Some bacterial infections can release toxins and lead to a shock-like syndrome – a condition known as toxemia.
Final Word
Sinuses are cavities around your nose and eyes that help clear your nasal cavity and keep it moist. Any inflammation in these cavities can cause nasal blockage and discomfort.
Acute sinusitis can be treated with decongestants and resolves in a few days. However, chronic sinusitis requires long-term treatment. Rest, increased fluid intake, and warm compress can help provide relief from sinusitis infections.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


