In this article:
Hiccups are a common nuisance and generally resolve on their own and don’t pose any serious health threat.

They can be described as sudden, rapid, uncontrollable contractions of the diaphragm, which is the dome-shaped muscle located under the lungs and above the stomach. (1)
Each spasm shakes the inspiratory muscles and the chest and is followed by the momentary closure of the vocal cords, which produces the characteristic “hic” sound as the incoming air gets blocked and is forcefully expelled.
Hiccups can be of three types depending on how long they last:
- Transient hiccups go away within a few seconds or minutes.
- Persistent hiccups go on for more than 2 days.
- Recurrent hiccups are characterized by repeated episodes that last longer than normal transient hiccups.
In most cases of self-limiting transient hiccups, the exact cause is generally unknown, but they are broadly the result of stomach distension or disturbances in the nerve pathways between the brain and diaphragm.
Common triggers of transient hiccups include: (2)
- Swallowing too much air while chewing gum, sucking candy, or eating too fast
- Overeating
- Intake of spicy foods
- Consumption of carbonated beverages
- Excessive smoking
- Excessive alcohol intake
- Sudden temperature fluctuations inside the gastrointestinal tract caused by eating cold food followed by hot food or vice versa, taking a cold shower, cold weather, etc.
- Sudden excitement
- Emotional stress, fear, or anxiety
All these factors can irritate the diaphragm in such a way that it contracts in a jerky manner, which leads to the sudden forceful sucking of air into the throat.
Persistent hiccups, on the other hand, are mostly triggered by more serious underlying factors including:
- Gastroesophageal conditions
- Cardiovascular disease
- Thoracic disorders
- Side effects of certain medications
- Irritation of the vagus nerve (linking the brain to the stomach) or phrenic nerve (linking the neck to the diaphragm)
The treatment for persistent hiccups depends on the root cause.
Home Remedies for Hiccups
Here are some quick and easy ways to get rid of hiccups.
1. Hold your breath

Hiccups usually start during inhalation and tend to subside when there is a buildup of carbon dioxide inside the lungs.
The carbon dioxide retention creates a positive airway pressure that relaxes the contracted diaphragm and causes the hiccups to cease. This mechanism forms the basis of some common nonpharmacological interventions used for controlling hiccups such as holding your breath. (3)
There is a specific breathing technique called supra-supramaximal inspiration, which increases the carbon dioxide levels inside the lungs. It can be done in the following way: (4)
How to do:
- Draw in a deep breath and hold it for 10 seconds.
- Without releasing your breath, inhale again and hold for 5 seconds.
- Draw another sip of air and hold for 5 more seconds before exhaling.
2. Breathe into a bag

Another easy and effective way to elevate the amount of carbon dioxide in the body is to breathe slowly and deeply while tightly holding a small paper bag over our nose and mouth. This will make the diaphragm pull down more deeply to suck in more oxygen, thereby stopping the hiccups. (1)(3)
3. Plug your ears
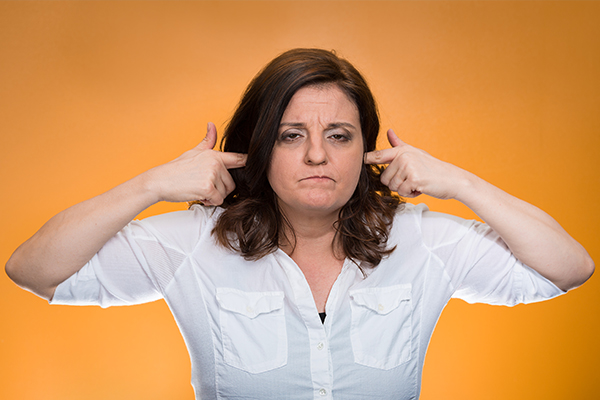

Inserting your fingers in your ears for 20–30 seconds or pressing the soft area behind your earlobes at the base of the skull stimulates the vagus nerve to send a relaxation signal to the diaphragm which ceases the spasms. (1) This may also help distract your brain from the hiccups.
4. Massage your neck (carotid sinus massage)

Carotid arteries run through either side of the neck and carry blood to the brain, neck, and face. Gently massaging each side of the neck one after the other for 5–10 seconds can help relax the vagus nerve to stop transient hiccups. (5)
However, this technique is generally ineffective against persistent hiccups. (6)
Note: A carotid sinus massage is not safe for people who have:
- Suffered a heart attack or stroke in the last 3 months
- A history of serious disturbances of the heart rhythm (such as ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia)
- Experienced adverse reaction to a previous carotid sinus massage
5. Drink water in a different way

One of the most popular tricks for treating hiccups is by drinking water while bending over a sink or titling your head upside down and sipping from the opposite side of the glass than you normally would.
This method works by stimulating or blocking some of the nerves involved in causing hiccups. (7)
6. Hold granulated sugar/ice chips in your mouth
This is another type of vagal maneuver that relaxes the diaphragmatic contractions to stop the hiccups. (4) Plus, it makes your mind focus on something else other than the hiccups, which allows the diaphragmatic spasms to cease quickly.
- Keep a teaspoon full of white or brown sugar or ice chips in your mouth and let them dissolve slowly without chewing.
- Sip some water thereafter and watch your hiccups go away.
7. Chew lemon
The strong taste of lemon can distract your brain away from the hiccups and overwhelm the irritated nerves that cause them. Plus, you will be compelled to gulp down its sour juice with force, which can make the hiccups stop instantly. (8)(7)
How to use:
- Simply bite or suck on a lemon wedge. Soaking it in a nonalcoholic bitter or sprinkling some salt on it can further enhance its pungency and lead to faster results, but this is optional.
- Swallow half a teaspoon of undiluted lemon juice.
- Mix the juice of one lemon in a half-full glass of water and drink this solution quickly.
8. Eat peanut butter
Peanut butter takes time and effort to be digested by the body. Chewing and ingesting a spoonful of this thick paste changes your swallowing and breathing pattern in such a way that makes your hiccups go away.
The vagus nerve gets overwhelmed by the task of gulping down and digesting the peanut butter and, in the process, stops irritating the diaphragm. This is the working theory behind this remedy, but more research is needed to understand the exact mechanism. (7)
9. Smell salts, vinegar, or pepper
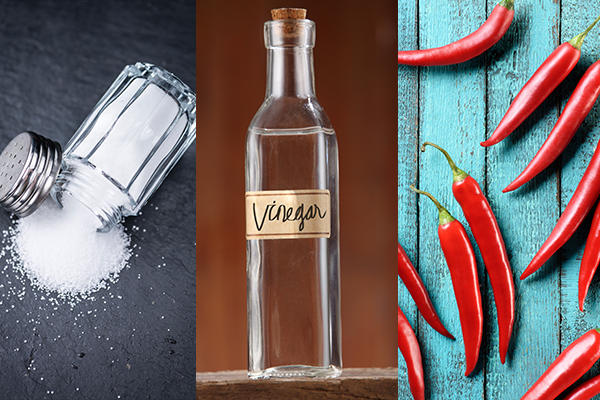
Smelling salts, vinegar, or pepper will induce sneezing (7) by stimulating the uvula or posterior nasopharynx, which is the top part of your throat (pharynx). (4) Sneezing can help loosen up the diaphragm and eliminate the hiccups.
10. Additional techniques for vagal stimulation
You can induce vomiting by activating your gag reflex, apply a cold compress to your face, pull your tongue, or have someone shock or frighten you – all of these help distract your brain from the hiccups and overwhelm the vagus nerve to stop the hiccups quickly.
Other Treatment Modalities for Hiccups
The above-mentioned remedies and maneuvers merely help in shortening the duration of acute transient hiccups, but they do not work on persistent or recurrent hiccups. (5)
If they fail to provide relief, you can try the following:
- Acupuncture
- Rectal massage
- Sexual stimulation and ejaculation
- Hypnosis
- Smoking marijuana (5)
Medical interventions to treat chronic hiccups include:
- Drugs including chlorpromazine, prokinetic agents, gabapentin, lidocaine, baclofen, and serotonergic agonists
- Anesthesia or surgery to disable the phrenic nerve
- Surgically implanted electronic stimulator for the vagus nerve
When to See a Doctor
Consult your doctor if your hiccups:
- Persist for more than 3 hours
- Occur frequently
- Are accompanied by intense abdominal pain, labored breathing, intense choking feeling, or blood in spit
Prolonged, frequent, or chronic hiccups, if left untreated, can cause sleeping difficulties, start affecting your speech, and make it difficult to keep your food and drinks down, resulting in malnutrition, dehydration, and rapid weight loss. In extreme cases, they may even prove fatal.
Final Word
Hiccups are generally not a health concern and do not require medical attention. You can wait for them to subside on their own or try the techniques mentioned above for rapid relief.
However, if the problem persists for too long or occurs too frequently, you must visit your doctor for the proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


