In this article:
Nausea is a queasy sensation accompanied by the tendency to vomit that most people have experienced time and again. Vomiting, or the involuntary expulsion of stomach contents, is preceded by a disagreeable painless sensation that is termed as “nausea.”

When a pathogen or a toxic element enters your body, it springs into defense mode to combat the incoming threat. Nausea and the subsequent vomiting are your body’s ways of expelling these undesired agents, along with the rest of the stomach contents, out of your system.
Nausea can make you feel uneasy, sweaty, and hot, although it may or may not necessarily result in an episode of vomiting.
Causes of Nausea
Nausea is not an illness per se but a symptom of a wide range of health problems. It can be caused by various reasons, such as:
- Painkillers
- Sunstroke
- Excessive daily consumption of alcohol
- Inadequate sleep
- Medications for cardiovascular diseases
- Cancer chemotherapy
- Anesthetic agents
- Bowel obstruction
- Brain problems
- Migraines
- Dehydration
- Motion sickness
- Oral contraceptives
- Menstrual cycles and pregnancy
- Post-operative periods
- Certain medications on an empty stomach
- Gastrointestinal discomforts such as acid reflux and GERD, non-ulcerous dyspepsia, heartburn, gall bladder infections, hepatitis, and diverticulitis
- Infections such as food poisoning, pneumonia, ear infections, meningitis, and kidney and bladder infections
Signs That You Are Nauseated
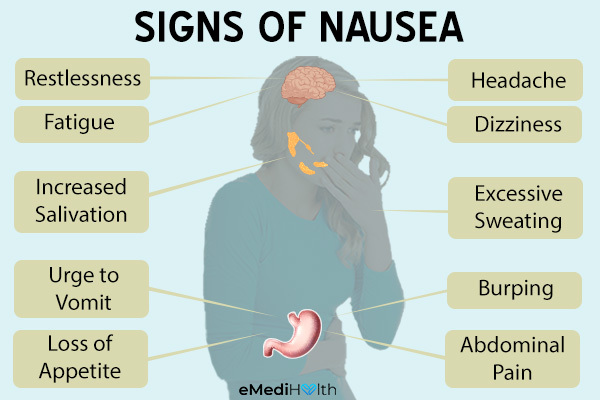
Symptoms associated with nausea include:
- Urge to vomit
- Increased sweating
- Repeated involuntary contractions in the gastrointestinal muscles
- Increased salivation
- Feeling restless
- Feeling of fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Burping
- Pain in the abdomen
Medical Treatment for Nausea
Although nausea can be easily diagnosed because of its associated symptoms, persistent chronic nausea calls for urgent medical intervention to identify the underlying health problem.
Nausea does not always require treatment, but sometimes, treatment is helpful. The treatment would differ according to the cause and severity of the condition: (1)
- Antiemetic drugs can help reduce nausea that would precede vomiting. Mild to moderate nausea can be treated with bismuth subsalicylate, prochlorperazine, or metoclopramide. These medications must not be given to children below 12 years or individuals suffering from chickenpox and flu.
- Antihistamines, scopolamine patches, or both may be prescribed for nausea induced by motion sickness.
- Since severe nausea can lead to vomiting-induced dehydration, oral rehydration solution and adequate water must be consumed to maintain proper fluid balance. Serious cases can be managed with IV fluid therapy (0.9% saline 1 L or 20 mL/kg in children).
Diagnosing Nausea
The foremost concern of the doctor in treating a severe case of nausea and vomiting is to identify and treat any harmful consequence of the condition, such as dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
This is followed by identifying the root cause of the problem, which is usually done by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical exam.
Further diagnostic tests are only needed when this preliminary investigation proves inconclusive or to assess any complications that may have arisen from your condition. This includes the following diagnostic tests:
- Blood work
- Esophageal manometry
- Wireless capsule gastrointestinal monitoring
- Gastroduodenal manometry
- Gastric emptying study
- Autonomic function tests
Complications of Nausea

Although nausea is not an illness, it can be serious if you experience the following:
- Severe headache or pain in the chest or abdominal area
- Stiffness in the neck
- Vomiting for the last 24 hours, causing weakness or fainting
- Dehydration causing infrequent urination
- Excessive weight loss due to prolonged loss of appetite
- Blood in your vomit
- Unclear vision or dry mouth
- Severe and persistent nausea accompanied by vomiting while pregnant
Severe nausea can cause vomiting. Persistent and uncontrolled vomiting can lead to electrolyte and fluid imbalance, dehydration, loss of energy, and nutritional deficiencies that can take a toll on the affected person’s health.
Symptoms of dehydration include:
- Reduced urge to urinate
- Frequent thirst
- Paleness
- Feeling of exhaustion
It is advised that you seek medical evaluation immediately.
Expert Answers (Q&A)

Answered by Dr. Subramaniam Ramakrishnan, MD (Gastroenterology)
Stress can lead to a number of physical symptoms, including nausea. Anxiety and stress can trigger the nerves that connect the brain and the digestive system. This action results in the release of chemicals that, in turn, cause nausea or vomiting.
Diabetes, which is a result of high blood sugar, can remain asymptomatic or cause a variety of symptoms. Nausea and vomiting may be one of the initial symptoms, especially in the younger population.
When levels of blood metabolites, such as sugars, urea, and ammonia, are significantly increased, they reach the brain center called the chemoreceptor trigger zone (nausea/vomiting center). This triggers a series of connections from the brain to the digestive system, resulting in nausea/vomiting.
Constant nausea could be one of the symptoms of cancer, although this in isolation does not immediately mean that cancer is the cause.
One of the most common problems that people with nausea face is that they do not feel hungry. Even if they do, the fear of eating may aggravate the problem. This may be the case for some people with any food that they try to eat, but in others, this can vary.
In most people, foods that are associated with strong smells, difficult to digest (greasy, fatty food), and very spicy may aggravate their symptoms. Additionally, eating very quickly may trigger nausea.
Most people feel better sticking to eating bland and cold foods with small bites and chewing slowly to relieve symptoms.
Cold foods or drinks are well known to suppress nausea. Aerated drinks and any food or drink ingested slowly can also reduce symptoms.
When these food items are consumed, there may be a reduction in the stimulation of the nerves of the digestive system that triggers nausea symptoms. However, the exact mechanism of how this works is still a matter of debate.
– Eat and drink slowly, taking adequate time to chew the food.
– Avoid greasy, fatty, fried, or spicy food items.
– Avoid stimulants. Caffeine is a common stimulant and is mainly found in tea and coffee.
– Attempt some distractions such as listening to music and watching television.
– Eat small meals at frequent intervals rather than eating one or two large meals in a day that are difficult to digest.
– Keep your eating environment clean, cool, and comfortable with a fresh flow of air.
– Try supplements that contain ginger or peppermint, which are known to reduce nausea.
– Avoid eating too close to sleeping time.
– Avoid wearing tight-fitting clothes.
– Avoid alcoholic beverages.
Final Word
Although nausea is not a very serious cause of concern, it may plague you with a feeling of fatigue. Since nausea is usually a symptom of an underlying health issue, it is very important to be aware of your condition.
Mild nausea may be curbed within a few hours by following simple remedies. However, if you experience nausea for 24 hours or more, seek immediate professional help. When experiencing nausea, it is important to rest the stomach, eat bland foods, and bulk up on clear fluids to avoid dehydration.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


