In this article:
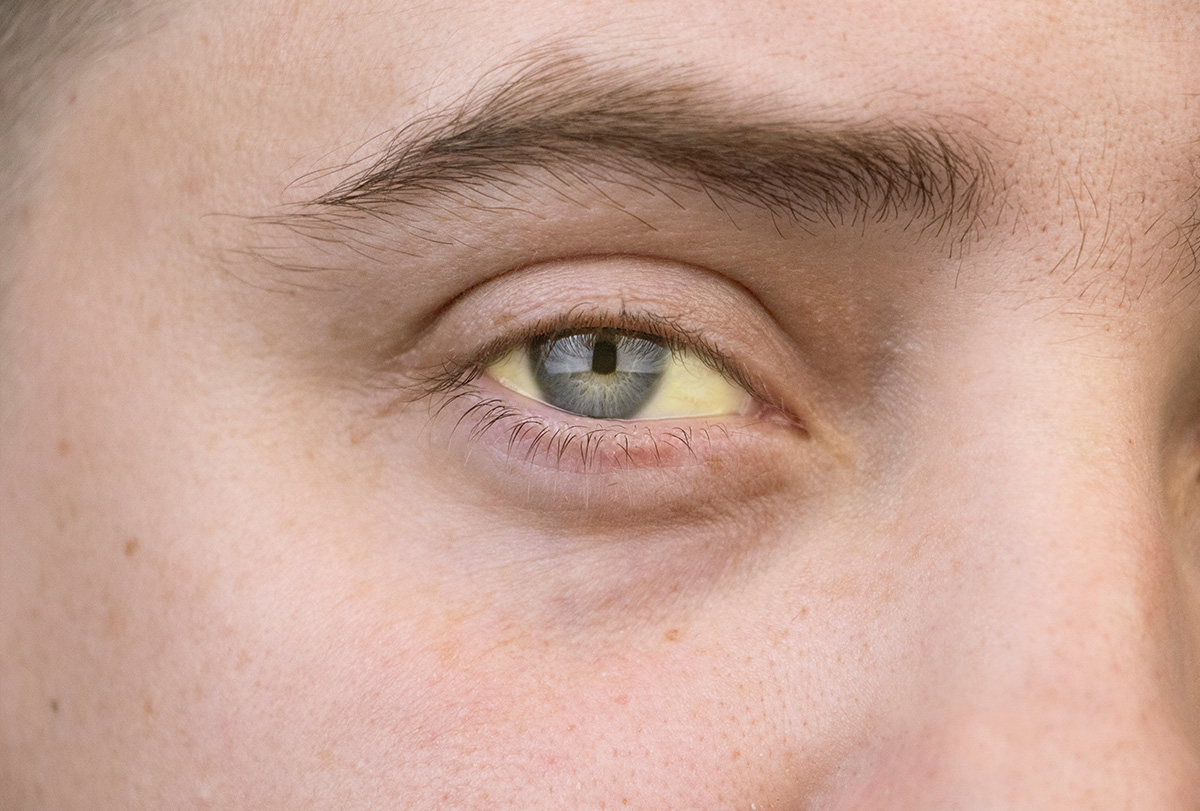
Jaundice is a condition in which the color of the skin and whites of the eyes and other mucous membranes turn yellow. The yellowing is due to the increased levels of bilirubin in the body.
Bilirubin is a pigment produced from the breakdown of red blood cells. The liver processes bilirubin and passes it through bile ducts into the intestine. Jaundice can happen from increased bilirubin production, decreased filtration through the liver, or blockage of the bile ducts.
Different Types of Jaundice
Jaundice can mainly be divided into three types:
- Pre-hepatic: Increased production of indirect bilirubin from increased destruction of red blood cells
- Hepatic: Increased direct or indirect bilirubin from liver dysfunction
- Post-hepatic: Increased direct bilirubin from blockage of bile from the liver into the intestine
Main Causes of Jaundice

Bilirubin is released in the blood as a by-product of the daily breakdown of red blood cells. This primary form of bilirubin is called indirect bilirubin, which cannot be directly excreted from the body.
Indirect bilirubin is filtered from the blood by the liver and converted into direct bilirubin, which forms a major part of bile. Bile passes through the bile ducts into the small intestine and is eventually excreted along with feces or urine, while some of the bilirubin is reabsorbed in the blood.
Jaundice happens when there is any defect or hindrance in this filtering process leading to a buildup of bilirubin. The causes of jaundice can range from minor problems with no symptoms or consequences to more serious ones.
1. Increased bilirubin production
Hemolytic anemias can cause jaundice. In this condition, there is increased destruction of blood cells which leads to a spike in bilirubin and internal bleeding called a hematoma.
2. Liver dysfunction
If the liver is diseased due to an inflammation called hepatitis, which can be due to:
- Viruses such as hepatitis A, B, C, and D, herpes, cytomegalovirus, and many others
- Excessive alcohol intake: which is defined as more than 7 drinks/week in women and more than 14 drinks/week in men can be toxic to the liver and can cause liver damage and jaundice.
- Mushroom poisoning
- Medications and drugs, such as Tylenol
- Autoimmune diseases
- Slow inflammation leading to scarring called cirrhosis
- Liver tumors
- Liver cancer: can cause jaundice by blocking the bile ducts (obstructive jaundice) or by destroying the normal function of the cells of the liver (liver infiltration) and decreasing the liver’s processing ability for bilirubin.
- Metastatic tumors in the liver, which can destroy normal liver cells and decrease the liver function
3. Blockage of bile ducts
If the flow of bile from the liver to the intestine is interrupted due to blockage of the bile ducts, which can be caused by gallstones, tumors, strictures, and pancreatic cancer.
Characteristic Symptoms of Jaundice

Excessive bilirubin can manifest visibility in the following ways:
- The whites of the eyes are the first to turn yellow.
- Your skin may also acquire a pale yellowish tint or even turn slightly greenish at high levels.
- Your urine may appear darker than usual.
This yellowish discoloration is unlikely to appear when the buildup of bilirubin is still relatively low. In such mild cases, lab tests are the only way to detect jaundice.
People with jaundice can also suffer from:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Itching
- Weight loss
- Fevers depending on the cause of jaundice
Normal Bilirubin Level
- Bilirubin, total: 0.0 to 1.0 mg/dl
- Bilirubin, direct: 0.0 to 0.4 mg/dl
Diagnosing Jaundice
Jaundice can be diagnosed based on physical examination from the yellow color of the skin and whites of the eyes (sclera), which is confirmed through certain lab tests. (1)
Healthy Lifestyle to Overcome Jaundice

If someone has jaundice or liver disease, then the following lifestyle changes are a must:
- Limiting alcohol
- Avoiding excessive medication use, such as excessive intake of Tylenol (>2 gm/day), which can lead to liver toxicity
- Consuming a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and protein, which is also good for your liver (2)
Signs That Jaundice Is Getting Better
Clearing of the yellow color of the skin and eyes is consistent with improving jaundice. Further diagnostic testing can reveal how better jaundice has become.
Recovery Period for Jaundice
This depends on the cause. Some conditions are reversible and jaundice can resolve if the underlying cause resolves, such as hepatitis A, a drug or toxin reaction, and blockage of the bile duct, which can be unblocked. However, many liver problems, such as hepatitis B and C and liver cirrhosis, are chronic and can be long-lasting.
Can Natural Remedies Help Cure Jaundice?
The causes of jaundice are quite extensive. Hence, the treatments are quite different. But there is no evidential support for any natural remedy that can cure jaundice.
Ways to Prevent Jaundice

The following measures can help keep you safe from jaundice:
- Avoiding risk factors that cause liver diseases, such as avoiding excessive alcohol intake and use of intravenous drugs, which are risk factors for viral hepatitis.
- Getting immunization for hepatitis A and B, which is recommended to all newborns in the USA and also adults who are not immunized previously.
Complications of Untreated Jaundice
As some of the causes of jaundice can be life-threatening, early assessment is very important. If there is any delay in assessment and treatment, the disease can progress and can lead to poor health outcomes. (3)
Most-Asked Questions About Jaundice
Is jaundice a fatal disease?
Jaundice is a symptom of many diseases, which can range from benign or mild without any major impact on body function to very dangerous and fatal diseases.
Is neonatal jaundice a serious condition?
Low levels of increased bilirubin may be benign. However, high levels of bilirubin (>25 mg/dl) in neonates can cause brain damage. (4)
Can jaundice relapse?
Yes, depending on the reason. Any chronic liver disease can get worse and cause recurring jaundice.
Is jaundice contagious?
Yes, jaundice can be contagious if it is caused by an infectious disease such as viral hepatitis, bacterial sepsis, or leptospirosis.
Hepatitis A can spread through food, whereas hepatitis B and C usually are contagious through blood or body fluids including intravenous drugs use, tattoos, blood transfusions, mother to fetus transmission, and sexual transmission.
Final Word
People of all ages can develop jaundice due to a wide variety of reasons, which may be benign or serious. It is imperative to get yourself medically evaluated at the earliest sign of trouble to rule out any serious underlying cause.
Excess bilirubin can be highly toxic, and timely treatment is key to avoid long-term liver damage or other potential complications.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


