In this article:
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is one of the most prevalent gastrointestinal disorders that hamper the functioning of your gut and, as a result, trigger a lot of digestive distress.

How Common Is It?
According to the American College of Gastroenterology, IBS is very common in the United States. Around 10%–15% of adults experience IBS symptoms but only 5%–7% have been diagnosed with it. One in five Americans suffers from IBS.
Even at the global stage, IBS has emerged as one of the most prevalent gastrointestinal disorders. (1)
Types of IBS
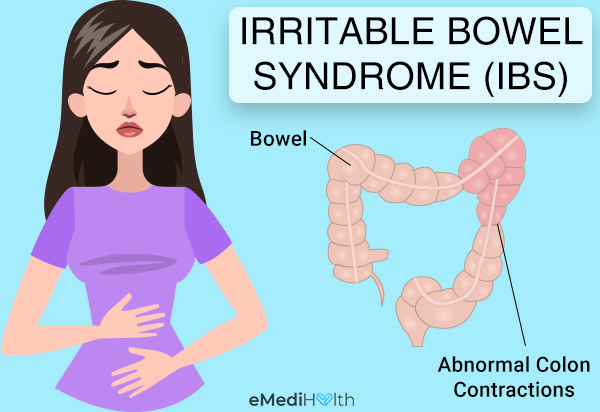
IBS is classified into three types. These include:
1. IBS-C (constipation-predominant)
The person alternates between constipation and normal stools. Eating may cause abdominal spasms or severe pain.
2. IBS-D (diarrhea-predominant)
The patient suffers from diarrhea soon after getting up or after he/she eats something. Sometimes, the bowel movement may be involuntary, and the person may need to make frequent urgent visits to the toilet.
3. IBS-A or IBS-M (alternating constipation and diarrhea)
This is an erratic form of IBS, which is characterized by at least one abnormal bowel movement in a day that may lead to constipation or diarrhea.
Thus, IBS-A is a mixed bad wherein you have not set pattern of bowel activity. Nearly 25% of such IBS episodes result in hard or lumpy stools, while another 25% are accompanied by runny stools.
Signs and Symptoms of IBS
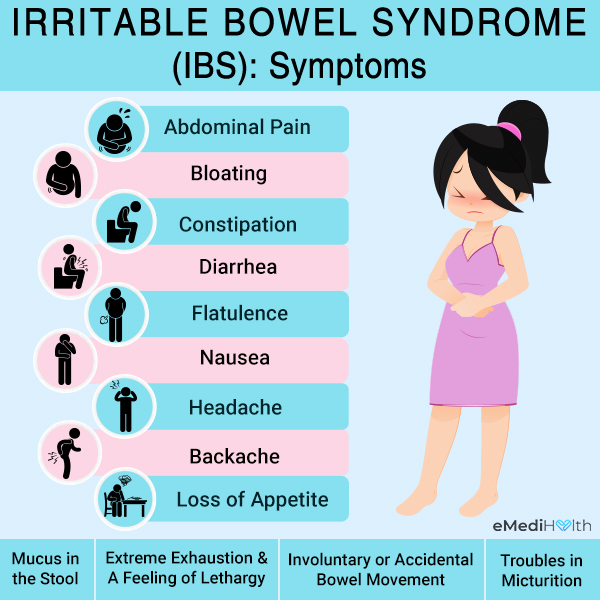
Chiefly, IBS presents with a change in bowel habits and chronic abdominal pain. Pain is usually related to defecation. The majority of patients report improvement in symptoms with defecation, while some patients report worsening of pain.
Emotional stress and certain dietary ingredients exacerbate the pain. Pain is also reported secondary to bloating and excess gas production.
Patients with IBS may often experience spasms or abrupt contractions of the colon muscles, which may come in waves and induce abdominal pain. Sometimes, the colon muscles may become hyperreactive or contract excessively, usually in response to stress or eating.
Some other common symptoms of IBS are:
- Flatulence and bloating – An uncomfortable feeling that your belly is swollen or full
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Flatulence
- Nausea
- Headache
- Mucus in the stool
- Backache
- Extreme exhaustion and a feeling of lethargy
- Involuntary or accidental bowel movement
- Troubles in micturition – frequent/sudden need to urinate; feeling as if your bladder is never free
- Changes in appetite
Risk Factors: What Are the Common Triggers?

Several factors can lead to IBS:
- Gender: Women are twice as likely to develop IBS as men, supposedly due to the hormonal changes they undergo during their menstrual cycle. (2)
- Smoking: IBS symptoms tend to be worse among people who smoke or those who are regularly exposed to secondhand smoke, with nicotine being the major irritant.
- Genetic factors: If IBS runs in your family, you are highly likely to develop it too since it’s often passed on through generations.
- Stress: Frequent stress, anxiety, and tension increase your risk of developing IBS and induce flare-ups.
- Food intolerance: Any kind of food intolerance or allergy can also lead to the onset of IBS symptoms.
- Constipation: Any hindrance in the passage or movement of stools through the digestive tract can set the ground for IBS.
- Oversensitivity: People with naturally oversensitive intestines are more prone to IBS.
- Altered hormonal regulation: A spike in the estrogen level is associated with increased severity of abdominal pain in patients with IBS.
Possible Complications
The discomfort aside, IBS does not pose any serious threat to your life. However, if you fail to manage the condition properly, it may give rise to the following complications:
- Patients with IBS who also have hemorrhoids may experience increased pain and discomfort in the rectum or anal region induced by frequent bouts of diarrhea or constipation.
- Prolonged constipation in patients with IBS can result in fecal impaction or progressive hardening of stools that remain stuck in the colon. The longer the stool remains in the colon, the more solidified it becomes. Hardened stools are extremely painful and difficult to pass.
- The persistent or repeated spells of diarrhea drain fluids out of your body and can leave you severely dehydrated.
- Living with IBS symptoms can take a toll on your emotional or mental well-being and pave the way for depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
- IBS symptoms can surface at any time or place and send you running to the nearest toilet, thus proving to be quite a handicap when venturing out. This unpredictable condition can hamper your overall quality of life by impeding your daily activities, work, and social life.
When to See a Doctor
A physician is to be consulted first so that he can review your symptoms and check if there is anything serious. He/she may then refer you to a gastroenterologist if need be.
Consult a physician if:
- You have a swollen abdomen.
- There is bleeding from the anus, or you have bloody stools.
- There has been a visible loss in weight.
- You have a breathless episode.
- You have pale skin.
- You experience heart palpitations.
Once you have been diagnosed with IBS, you must consult a gastroenterologist if:
- There is considerable loss in your weight with constant fever.
- You have bloody stools.
- You suffer from pain in the abdominal region, along with dizziness, fainting, and vomiting.
- Your sleep was disturbed due to a bout of diarrhea.
- Additionally, the following factors may contribute to the need for further testing/evaluation on a case to case basis: onset above the age of 50, nocturnal diarrhea, rectal bleeding, aggravating abdominal pain, laboratory abnormalities, weight loss, and/or family history of IBD or GI cancers.
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Dr. Subramaniam Ramakrishnan, MD (Gastroenterology)
No. The Rome IV diagnostic criteria for IBS include abdominal pain but this has to be associated with two or more of the given criteria:
– Related to changes in bowel movements
– Change in the form of stools
– Change in the frequency of stools
Additional criteria include that the symptoms have to be recurrent on average at least once a week in the last three months and with the onset of symptoms for at least 6 months.
Evidence for the role of caffeine in gastrointestinal disorders is quite varied.
Some studies show caffeine to be the cause of stimulating intestinal motility and therefore worsening the condition of patients who have bowel frequency as their predominant IBS symptoms. (3)
Yes. There are excellent studies that correlate stress to IBS symptoms and, interestingly the converse, that is, relief of IBS symptoms when stress is reduced.
Eggs are one of the dietary components that have been associated with the flare-up of IBS symptoms in some patients. It is recommended as part of an elimination diet to help them.
There is strong evidence to point to hereditary factors in IBS as studies in monozygotic twins show a high concordance as compared to dizygotic twins.
Additionally, many family clusters of functional gut problems also known to exist, provide evidence of a genetic predisposition. (4)
Weight gain is not a usual feature of IBS. However, some patients who have bloating as a significant symptom also report weight gain. Treatments for IBS with antidepressants may also result in weight gain.
IBS is a condition without any significant or visible changes to the digestive system. IBD, on the other hand, results in inflammation, ulceration, narrowing, or widening of the digestive system. Treatments of these conditions are also very distinctive, but some overlap exists in certain patients.
While the diagnostic criteria for IBS are well defined, and patients may be classified as having this condition, one has to be careful not to miss IBD diagnosis as both conditions may coexist.
Final Word
IBS is a lifelong condition that causes a lot of digestive distress but no real damage to your digestive tract or any other serious health concerns.
However, if left untreated, can negatively impact your appetite and thereby your overall nutritional status. Moreover, it can take a heavy toll on your mental and emotional health. Therefore, it is important to seek timely treatment to keep the symptoms under control and preserve your general wellbeing.
While it is difficult to recommend any preventive measures, consuming a well-balanced diet, avoiding the triggers, and regulating your stress levels may help in effective management of the symptoms.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY



