In this article:
Gallstone pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas that occurs when a gallbladder stone blocks the pancreatic duct. (1) This condition can be quite painful, and its seriousness can range from mild to potentially dangerous.

Early treatment at the first sign of trouble is recommended to minimize the damage and pain and also to prevent undue complications later. Here’s everything you need to know about the development, manifestation, and treatment of gallstone pancreatitis.
The Function of the Pancreas
The purpose of the pancreas is to aid in digestion. The pancreas produces enzymes that break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
The pancreas also creates hormones called insulin and glucagon, which are responsible for maintaining blood sugar balance. Thus, the pancreas plays a role in diabetes. When the pancreas cannot create insulin, the affected individual is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus type 1.
Formation of Gallstones and How They Cause Pancreatitis
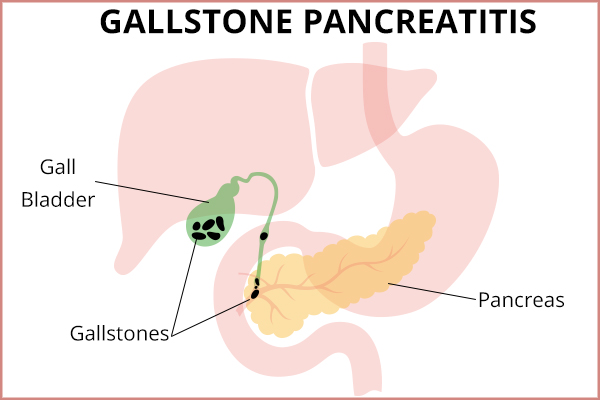
If you think of the gastrointestinal tract in terms of plumbing, the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas have their own drains, also known as “ducts.” All three of these ducts merge into one tube before emptying their contents into the small intestine.
Sometimes, the gallbladder will have a complication where it forms solid granules made of bile salts, commonly known as “gallstones.” If the gallbladder ejects one of these stones, the stone will travel down its duct and will lodge downstream where the duct of the pancreas drains.
This can cause a blockage in the system, similar to flushing an inappropriate item down the toilet, leading to a clog where all the other plumbing pipes converge. A blockage in the area where the pancreas drains its contents will cause an inflammatory response called “pancreatitis.”
Signs and Symptoms of Gallstone Pancreatitis
Gallstone pancreatitis is certainly a concerning diagnosis. As with most conditions, gallstone pancreatitis can range from very mild to very severe.
Most of the gallstones pass into the small intestine, and the symptoms disappear or never appear in the first place. The most common symptom of this condition is abdominal pain.
If someone already knows they have gallstones, the pain may be similar to their usual flare-ups. However, when the pancreas is also involved, the pain may radiate from the abdomen to the back. The pain may also be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sweating, fever, and chills.
However, in more serious cases where the stones continue to block the duct, the affected individual can become severely ill and may require intensive care treatment.
Treatment Modalities for Gallstone Pancreatitis
The good news is that gallstone pancreatitis is treatable. Surgery is the only solution for gallstone pancreatitis.
If your doctor finds that a gallstone is indeed blocking the drainage of the pancreas, an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) will be performed. (2) This procedure sounds very fancy. However, it simply involves inserting a scope down your mouth into the gut to retrieve the stone.
ERCP is essentially a temporary cure. As long as you have your diseased gallbladder that is making gallstones, you will remain at risk for future blockages and subsequent pancreatitis.
The definitive treatment, in the end, is removing the gallbladder in a procedure called a “cholecystectomy.” (3) With the advancement of surgical procedures, this operation can now be performed as an outpatient.
Diagnosing Gallstone Pancreatitis
Your physician will be able to diagnose this condition through abdominal ultrasound in a majority of cases. Sometimes, a CT scan or MRI will be necessary to find the offending stone. Blood work will also show to what extent the pancreas is inflamed and if there is any compromise to the body’s organs.
Preventive Measures
Unfortunately, not much can be done to prevent gallstone pancreatitis. The best you can do is to maintain a healthy weight as those who are overweight are more likely to get gallstones.
Risk Factors for and Complications of Gallstone Pancreatitis
The risks of developing this condition are the exact risks of getting gallstones:
- Female sex
- Age over 40
- Family history of gallstones
- Pregnancy
- Rapid weight loss
- Diabetes
- Some medications
If left untreated, gallstone pancreatitis can cause severe infection (sepsis), organ failure, and even death.
When to See a Doctor
Talk to your doctor if you have ongoing abdominal pain of any sort. An abdominal pain that travels to the right shoulder or the back is likely a sign of gallbladder and/or pancreas inflammation and should be addressed immediately.
If you have these symptoms along with fevers, chills, vomiting, or sweating, go to an emergency room promptly.
Expert Answers (Q&A)
Answered by Dr. Gautamy Chitiki Dhadham, MBBS (Gastroenterologist)
Removing the gallbladder after acute gallstone pancreatitis prevents future attacks of pancreatitis but does not cure pancreatitis.
The treatment for pancreatitis involves intravenous fluids, pain medications, and fasting for 24 hours, followed by a slow introduction of clear fluids and advancing to “diet as tolerated.”
Yes, pancreatitis has many causes, such as alcohol abuse, high blood triglyceride levels, autoimmune medications, and viruses.
Gallbladder removal is advised in all patients who have acute gallstone pancreatitis after ruling out other etiologies, and a low-fat diet is usually recommended.
Yes, jaundice occurs if the stone is in the common bile duct and is obstructing bile flow. In these cases, the patient would first require an endoscopic procedure called endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to relieve the common bile duct obstruction before gallbladder removal.
Mild elevation of blood sugar can be observed in some cases.
Final Word
Gallstone pancreatitis is actually a gallbladder issue at its core. It can be a temporary and benign condition, or it can progress to serious illness.
Knowing the symptoms and risk factors of gallstones is essential because your doctor can make the diagnosis and recommend early removal of the gallbladder before it leads to complications such as pancreatitis.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


