In this article:
Soft tissue injuries refer to injuries of the tendons, ligaments, and muscles throughout the body.

Common soft tissue injuries usually occur from a sprain, strain, blow resulting in a contusion, or overuse of a particular part of the body. (1) Soft tissue injuries can cause pain, swelling, bruising, and loss of function in some cases.
These injuries usually occur during sports and exercise activities, but sometimes even simple everyday activities can cause such an injury too.
Types of Soft Tissue Injuries
There are various types of soft tissue injuries, which include contusions, sprains, strains, tendonitis, bursitis, and stress injuries. Soft tissue injuries can be further broken down into two categories:
- Acute injuries
- Overuse injuries
Acute injuries are the result of acute trauma. Sprains, strains, and contusions all fall under the category of acute injuries. Overuse injuries happen gradually over time and are caused by repetitive use of a specific area of the body.
As a result, the body fails to have time to heal, causing inflammation in that specific area. Examples of overuse injuries include tendonitis, bursitis, and stress injuries.
Common Acute Soft Tissue Injuries
The three most common acute soft tissue injuries are sprains, strains, and contusions. (2)
A sprain/strain is a tear and/or stretch of a ligament/tendon often caused by a sudden twisting force. This results in pain, edema, inflammation, and oftentimes bruising.
A contusion, also known as a bruise, is caused by direct blunt trauma to a specific area, causing erythema, edema, and discoloration of the skin. The discoloration of the skin is due to bleeding into the tissues.
Sprains and Strains and the Difference Between the Two
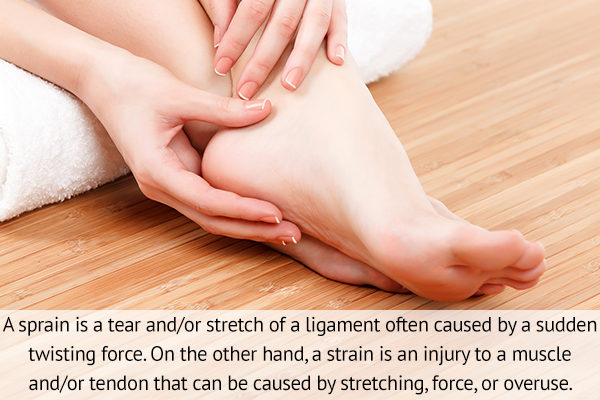
Sprains are injuries to the ligaments, whereas strains are injuries to the muscles and tendons.
A sprain is a tear and/or stretch of a ligament often caused by a sudden twisting force. (2) This results in pain, edema, inflammation, and oftentimes bruising. The knees, ankles, and wrists are the most vulnerable to sprains because these joints have various ligaments that attach the end of one bone to another.
There are three grades of sprains:
- Grade 1 or mild sprains are caused by stretching and mild damage to the fibers of the ligaments.
- Grade 2 or moderate sprains are caused by a partial tear to the ligament, resulting in abnormal laxity.
- Grade 3 or severe sprains are caused by a complete tear in a ligament, causing instability to the joint.
On the other hand, a strain is an injury to a muscle and/or tendon that can be caused by stretching, force, or overuse. (2) This can result in a partial and/or complete tear to a muscle and/or tendon.
One will experience pain, muscle weakness, edema, muscle spasms, cramping, and inflammation after sustaining a strain. The most common areas of the body for a strain to occur are the foot, leg, and hamstrings. The grading system for strains is similar to that of sprains.
Treatment of a Soft Tissue Injury

Treatment depends on the type of soft tissue injury. In general, the best initial treatment for a soft tissue injury is RICE, which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
An addition of an anti-inflammatory medication is often recommended. However, some soft tissue injuries require surgery. (3)
How Is Soft Tissue Injury Prevented?
Not all injuries can be prevented, but there are strategies to decrease their incidence.
Using the proper equipment, incorporating balanced exercise programs, warming up and cooling down properly, staying hydrated, stretching, and making sure you are giving your body adequate rest can help.
What Is the Difference Between Soft Tissue and Hard Tissue?
Hard tissue has a firm intracellular matrix. Examples of hard tissue are bone and teeth. Soft tissue connects, supports, and/or surrounds structures of the body. Examples of soft tissue include ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
How Long Does It Take for a Soft Tissue Injury to Heal?
Depending on where and how severe your soft tissue injury is, it could take weeks to months for a soft tissue injury to heal. (4) And if you are not following the proper instructions for your healing, the pain could last even longer than that.
If you need surgery, your healing regimen may differ, but many soft tissue injuries can heal through nonoperative treatments.
Can Soft Tissue Damage Be Permanent?
Most soft tissue injuries can heal or be fixed. Unfortunately, some soft tissue injuries may cause long-lasting disabilities. However, by consulting a medical doctor early on, you can decrease the chances of permanent damage.
Final Word
Soft tissue injuries involve damage to your muscles, ligaments, and tendons, which can cause a lot of pain, discomfort, and restriction of movement. You must exercise proper precautions when performing your exercise and daily activities to avoid such injuries, but even the most cautious people can get injured sometimes.
Fortunately, such injuries tend to heal completely with proper rest, self-care, and treatment. Early treatment is vital in minimizing tissue damage and the associated pain and disability and in ensuring fast and complete recovery.
The key is to rest the affected area without making it totally inactive. Ask your doctor or physiotherapist about the appropriate exercises to keep the damaged part active, or else the muscles in the area will start wasting away, and restoring full range of motion will be difficult.
Some injuries heal fast, while others may leave behind some degree of permanent damage. Whatever the case, don’t rush your recovery process and let your doctor guide you through it.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


