In this article:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition characterized by pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the joints. It can affect people of all ages and worsens over time. Therefore, it is vital to intervene at the earliest and take measures toward controlling this disease.
Home Remedies
The following home remedies can help manage the symptoms of RA.
1. Consume ginger tea

Ginger possesses anti-inflammatory properties that can relieve the swelling associated with arthritis. Moreover, it helps reduce T cell action that is responsible for the systemic inflammation. (1)(2)(3)
How to use:
Boil a few slices of fresh ginger with a cup of water and strain. Add lemon and honey to the tea according to taste and consume.
Caution: Excessive consumption of ginger can cause constipation and flatulence. Moreover, people with gall bladder issues should avoid using ginger.
2. Consume turmeric
Curcumin, the active compound of turmeric, inhibits the inflammatory enzymes and cytokines, thus alleviating joint pain and swelling. (4)(5)
How to use:
- Mix 1 teaspoon of turmeric in warm milk and consume.
- Use turmeric as a spice in curries.
- Massage your joint with turmeric oil.
- Take turmeric supplements after consulting your doctor.
3. Include omega-3 acids in your diet
Omega-3 fatty acids contain anti-inflammatory agents such as EPA and DHA that can help relieve arthritic inflammation. (6)(7)
How to use:
Consume 3–4 ounces of fish oil every week. You can also use flax, algae, or supplements upon consulting your doctor.
Caution: Consume moderate amounts of omega-3 as an excess can lead to mercury poisoning.
4. Apply a warm compress
The heat from a warm compress can help manage pain and RA flare-ups.
How to use:
- Apply a hot water bottle or an electric heat pad over your joints.
- You can also take a hot shower or bath.
Caution: Make sure that the compress is not too hot to cause scalding. It is best to wrap the compress in a towel before use.
5. Use a cold compress
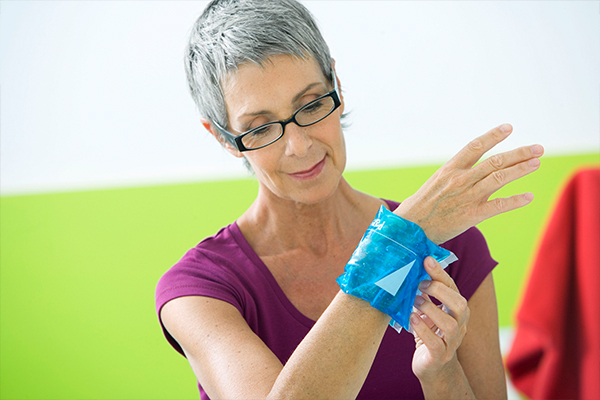

An ice pack may help relieve pain in some patients. The cold from the compress helps numb the area and desensitize the pain signals for some time.
How to use:
Wrap a few ice cubes in a wet tea towel and place it on your joints. You can also use a pack of frozen peas as a cold compress.
Note: Place a towel over your skin before applying an ice pack to prevent skin damage.
6. Consume antioxidants
Antioxidants play an essential role in reducing inflammation by boosting the immune system.
How to use:
- Consume 1–2 cups of antioxidant-rich fruits, such as blueberries, with every meal. (8)
- You can also eat foods rich in vitamins A, E, and C, selenium, zinc, and beta carotene.
7. Drink apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is a popular anecdotal remedy for managing RA. While there is no scientific literature on it, some patients support the consumption of ACV.
How to use:
Add 2 tablespoons of ACV in a glass of water and consume. You can also add this diluted liquid to your cooking.
Dietary Tips for Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis

The foods you eat play an important role in your health. Because people all differ genetically, no single dietary approach is optimal for all people. Therefore, each person with RA has to explore different dietary strategies to determine which is best for him/her.
In general, the Mediterranean diet, plant-based diets, paleo diets, and others may be beneficial. (9)(10)(11)(12) It is advised to follow an anti-inflammatory diet, which includes:
- Consuming whole and mostly plant-based foods with lean protein sources.
- Avoiding added sugars and artificial sweeteners as well as processed foods. Processed grains tend to be inflammatory.
- Minimizing foods in a box or most frozen meals. Reducing carbs, which include bread, bagels, muffins, crackers, pasta, and cookies (anything made with flour).
- Including green vegetables and cruciferous veggies as they are great sources of fiber and also provide numerous phytonutrients, antioxidants, vitamins, and polyphenols.
- Consider eliminating tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, almonds, cashews, walnuts, milk, dairy products, eggs, corn, soy, and legumes for a trial to see how arthritis responds.
Lifestyle Tips
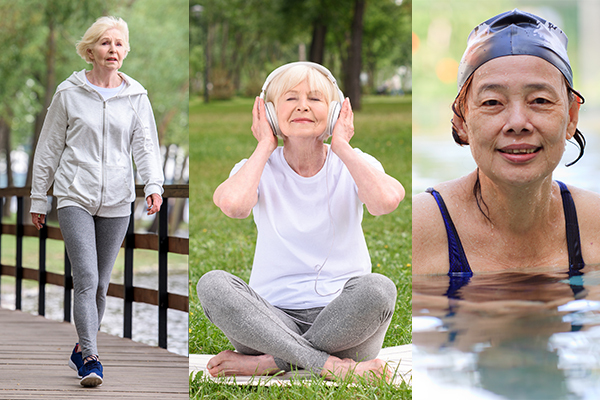

Modifying your lifestyle is an important step toward controlling the symptoms associated with RA.
- Regularly perform low-impact exercises, such as walking, yoga, and swimming, to help maintain joint function and neuromuscular tone.
- Avoid prolonged periods of inactivity as it can lead to the “gel phenomenon,” in which the joints become stiffer and set like gelatin due to the lack of movement.
- Get adequate sleep and manage stress, both of which can impact disease activity.
- Use self-help devices, such as reachers, jar openers, and easy-grip utensils, to take the load off your daily tasks.
- Massage your joints gently to help with the pain and movement.
- Establishing a relationship with a rheumatologist to help with disease management is very important.
Most-Asked Questions About Rheumatoid Arthritis
Are rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia different conditions?
Yes, they are very different. RA is an autoimmune condition primarily affecting the joints.
Fibromyalgia (FMS), on the other hand, is not a joint disease. Although patients with FMS experience significant musculoskeletal pain, the pain is generally widespread and diffuse and often affects the muscles, especially of the extremities and back.
Is rheumatoid arthritis hereditary?
Yes. RA has a clear familial association. A person with a first-degree relative with RA has about three times the risk of developing the condition, and those with a second-degree relative have double the risk. (13)
Can rheumatoid arthritis lead to multiple sclerosis?
Possibly. An association between RA and multiple sclerosis is not clear but has been reported. The data are mixed, but there may be a higher incidence of RA among patients with multiple sclerosis. (14)
Is rheumatoid arthritis curable?
Not presently. (15) But many medications are available that can control the disease, reduce the pain and joint swelling, and protect against joint damage over time.
Can rheumatoid arthritis affect other body parts besides the joints?

Yes. RA has many “extra-articular” manifestations, including:
- Rheumatoid nodules
- Tenosynovitis, or swelling of the tendons
- Scleritis and episcleritis
- Rheumatoid lung in which nodules and lung opacities may be seen on X-ray
- Rheumatoid vasculitis, in which inflammation progresses to involve the blood vessels, causing interrupted blood flow
- Sjogren’s syndrome, in which autoimmune inflammation affects the secretory glands of the body, leading to dryness
Is thunder god vine safe for managing rheumatoid arthritis?
Thunder god vine is a medicinal herb with anti-inflammatory properties. While some studies show a positive effect of its use in patients with RA, its safety has not yet been determined. Therefore, it is best to avoid using this herb as it can cause infertility, diarrhea, hair loss, rashes, and even poisoning.
Final Word
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when your immune system attacks the body’s healthy tissues, resulting in inflammation in the joints. While it cannot be cured, making changes in your lifestyle and diet can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


