In this article:
The knee is the largest joint of the human body and has a complex working structure. It consists of cartilage, bone, ligaments, and a small amount of synovial fluid. The movement of the knee is facilitated by the surrounding muscles and tendons.
Knee pain occurs due to the softening and breakdown of the cartilage in the underside of the kneecap (patella) or over the long bones (tibia and femur) as well as in the surrounding soft tissue structures triggered by repetitive stress injury.
Causes of Knee Pain
The common causes of knee pain include:
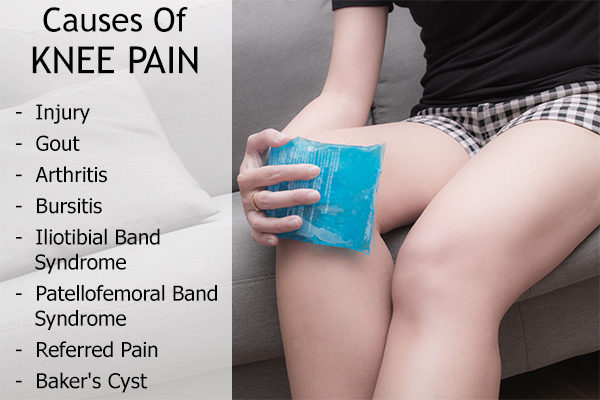
1. Injury
Knee pain may result from injuries such as:
- Sprained knee ligaments or muscles: A blow to the knee or a sudden twist can cause a sprain or strain on the knee muscles or ligaments.
- Torn cartilage: The cartilage around the kneecap may soften due to injury, muscle weakness, overuse, or misalignment of the knee. Additionally, a portion of the cartilage may tear off as a result of a blow to the knee.
- Tendonitis: An inflammation or tear in the tendons is known as tendonitis. One common form is the jumper’s knee, which occurs due to constant jumping, such as while playing basketball.
- Fracture: A fall or accident can cause the bones, including the kneecap, to break. People with osteoporosis can also fracture their knee with wrong, sudden movements.
- Meniscus tear: A twisted knee or direct contact can cause harm to the cartilage between your shinbone and thighbone (meniscus), resulting in severe joint pain. Plus, this cartilage gets thinner and becomes increasingly prone to degenerative tears with age.
2. Gout
A buildup of uric acid crystals in the knee can cause gout, a type of arthritis.
3. Arthritis
Arthritis refers to the inflammation of the joints and can cause swelling, pain, and stiffness. Arthritis of the knees can interfere with daily activities, creating problems while walking or climbing stairs and causing discomfort.
Gout is an example of arthritis. Osteoarthritis of the knee is a common mechanically driven arthritic condition.
4. Bursitis
Bursitis is a condition wherein the joints become swollen, painful, and tender. It can affect any joint, but it is more commonly seen in the hips, knees, shoulders, and elbows.
5. Iliotibial band syndrome
Iliotibial band syndrome refers to the swelling and irritation in the band of fibrous tissue on the outside of the thigh.
6. Patellofemoral band syndrome
Patellofemoral band syndrome is a prevalent cause of knee pain in young athletes and is commonly known as runners’ knee.
It occurs as a result of overuse from activities that causes pressure or friction, affecting the cartilage around the knee cap. It is frequently seen in players who participate in jumping, running or squatting sports.
7. Referred pain
Pain arising from problems in the hip joint can radiate down to the groin, leg, and knee. In this case, the knee pain is indicative of problems in the hip joint and is known as referred pain.
8. Baker’s cyst
A popliteal cyst, also known as Baker’s cyst, refers to a fluid-filled inflammation at the back of the knee. This is caused by swelling of the tissue behind the knee joint.
Note: Several other conditions can manifest knee pain as a symptom. Therefore, it is vital to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis.
Symptoms of Knee Pain
Knee pain usually manifests in the following ways:
- The onset of pain can be sudden or gradual, beginning with a mild discomfort and worsening over time.
- The pain tends to exacerbate while bending or straightening the knee, putting weight on it, walking, climbing, and even resting or sleeping.
Knee pain may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Bruising around the knee
- Swelling (in or around the joint)
- Stiffness
- Redness
- Warmth to touch
- Weakness or instability
- Clicking, cracking, or popping sounds in the knee
- Inability to straighten (extend) or bend (flex) the leg completely
- Locking of the knee joint
First-Line Treatment
If you develop knee pain and swelling in the wake of sudden trauma or injury to the joint, the first thing to do is apply the RICE treatment. RICE stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
It is a multifaceted approach that addresses various aspects of the joint damage to provide immediate pain relief, curb swelling, facilitate quick healing, and restore joint function and flexibility.
Read more about this technique in: How to Reduce Knee Pain at Home
Standard Medical Treatment
The common treatment methods for knee pain include:
- Physical therapy: Regular physical exercises can help alleviate the pain associated with arthritis as effectively as over-the-counter medications. It also provides other benefits such as improved physical function, anxiety, and mood.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: You may take painkillers, such as ibuprofen and paracetamol, if needed, as long as there are no safety issues for you to use these medications. Follow the prescribed dosage every day. Be sure to consult your doctor before starting any medications to make sure they are safe for use.
- Injection therapies: Cortisone injections and hyaluronic acid injections may be beneficial for reducing osteoarthritic knee pain. Research supports the use of cortisone for mild alleviation of the pain. However, newer data are showing some conflicting results. Thus, its use should be discussed with your physician. (1)
- Joint replacement surgery: An arthroplasty or total knee replacement surgery is performed to replace a diseased or damaged knee with an artificial one.
- Arthroscopic surgery: The damaged part of the synovium and cartilage is removed by using an arthroscope (endoscope) inserted into the knee joint.
- Chronic pain rehabilitation therapy: Rehabilitation programs are commonly advised for people with chronic pain, including knee pain. Although rehabilitation may not treat the condition, it helps manage the pain to ease daily activities.
Diagnosing Knee Pain
Identifying the cause behind your knee pain is a multi-step process.
1. Medical history
The doctor will first record your symptoms and go through your medical history, which includes prior episodes of knee pain or other knee problems, previous or preexisting illnesses/infections, conditions that run in your family, medications you are on or have taken recently, and any treatment or tests that you might have undergone in the past.
2. Physical exam
The doctor will then examine your knee while standing, sitting, and walking to confirm or rule out potential causes. Your knee will also be checked for any swelling, breaks in the skin, reddening, and bruising.
The doctor will also assess your knee alignment and check whether you have knock knees or bow legs.
The doctor may test the tightness and strength of your ligaments and tendons and your knee’s range of motion and stability by using specific tests and maneuvers.
3. Diagnostic tests
If the preliminary investigation is inconclusive, the doctor may order the following imaging tests to get an inside view of the knee joint:
- X-ray
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography scan (CT or CAT scan)
- Ultrasound
Risk Factors for Knee Pain
The following factors can increase your risk of developing knee pain:
- Previous knee injuries
- Obesity
- Repeated or continuous strain on the knee, common in people whose jobs involve kneeling, squatting or lifting heavy weights
- A difference in the length of both legs
- Knee problems such as knock knees or bowlegs can cause knee pain
- Autoimmune and inflammatory conditions (such as gout) affecting the knee joint or surrounding tissue
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor in any of the following cases:
- Severe pain
- Swelling in the knee
- Inability to move the knee
- Persistent pain
- Unable to put weight on the knee
- Locking of the knee
- Painful clicking
- Knee gives way
Final Word
Knee pain is a common problem that can occur in individuals of all ages, due to injury, trauma, or inflammation affecting any of the structural components of the joint.
While it is typical for the knee, or any other joint, to experience wear and tear with time, the functioning and movement of the joints should remain normal until significant structural changes occur.

- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


