In this article:
Back pain is a common and often chronic problem, which can wear your entire body out. This condition tends to be recurrent in nearly half the cases, which is why you must exercise caution even after the pain has resolved.
Home Remedies for Back Pain
Here are a few remedies for back pain that may not have a lot of scientific support, but have nevertheless proven helpful for many general users:
1. Apply capsaicin-based creams
Capsaicin is the chief compound found in chili peppers that releases heat in the body when ingested or used externally.
Cream formulations containing capsaicin have been commonly used to help alleviate different types of back pain, including muscle pain and some forms of spinal osteoarthritis. Such creams have minimal side effects and can be easily used at home. (1)
A 2016 meta-analysis demonstrated that capsaicin has ethnopharmacological potential. Therefore, it can be used as an adjunct treatment for neuropathic pain. (2)
Note: People who are allergic to chili peppers or those who have reacted negatively to topical capsaicin in the past should not try this remedy. Capsaicin application is bound to cause a little burning sensation, but discontinue its use if it makes your skin severely irritated or red.
Wash the affected skin with soap and cool water to get rid of the product completely. Seek medical help if you experience extreme stinging, swelling, pain, or blisters after using this remedy.
Topical capsaicin induces a burning sensation in the area of the application, and the heat stimulates certain nerve cells in such a way that you feel less pain.
2. Apply a warm or cold compress
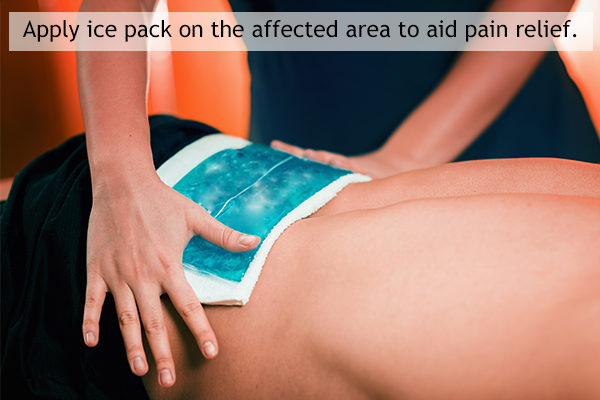
Applying a cold compress to the affected area can numb the pain temporarily by desensitizing the underlying nerves. Heat application through a heating pad, warm bath, or hot water bottle can stimulate blood circulation in the area and loosen the tight muscles.
You may use each of these therapies for 15 minutes every hour, alternating between cold and warm compresses for best results.
Thermotherapy and cryotherapy can help alleviate acute lower back pain, but mostly when used as an adjunct to standard medical treatment. (3)
3. Consume turmeric

The main component of turmeric is curcumin which is known to exhibit significant anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, both of which can help in reducing muscle pain. (4)
How to use:
- Incorporate turmeric in your regular cooking as it is a versatile spice that can enhance the flavor of many dishes.
- Drink turmeric milk, a popular healing tonic that can help alleviate various pain and repair worn-out muscles.
- Regularly consume turmeric tea to help ease back pain.
- Take turmeric supplements but only after consulting your doctor.
4. Use essential oils
Essential oils are therapeutic potions that can help relieve lower back pain, usually by curbing the underlying inflammation (5) or inhibiting the perception of pain by manipulating the neural pathways. These oils help soothe the body and uplift your mood, making you feel less pain.
Peppermint oil, lavender oil, (6) and copaiba oil have been found especially helpful in this regard.
How to use:
- Mix a few drops of your preferred essential oil with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil, and then apply it all over the painful area.
- Use essential oils for aromatherapy. Add a few drops of diluted essential oils into a diffuser and breathe in the soothing vapors for pain relief.
Caution: Essential oils are quite strong at their original potency and can severely irritate the skin. Make sure to dilute them first with a carrier oil before use.
5. Try apple cider vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is another popular remedy for back pain with a lot of anecdotal support but fairly little scientific backing.
It is suggested that the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of ACV may be responsible for its therapeutic effect, but further studies are needed to understand the exact mechanism and efficacy of this remedy in providing relief from back pain. (7)
How to use:
- Add a few drops of coconut oil to unfiltered ACV (with “mother”) to bring down its potency, and gently rub this mixture all over your lower back.
- Mix 1–2 tablespoons of ACV in a glass of water, and drink this tonic once a day to alleviate the symptoms of back pain.
6. Use MSM
Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is a credible anti-inflammatory agent that may help reduce lower back pain when taken orally or applied topically. (8)
How to use:
- Apply a topical MSM cream or gel to your back for pain relief.
- Take MSM dietary supplements either in powder or pill form but only upon consulting your doctor.
Alternative Treatment Options

Several alternative therapies may help reduce back pain.
1. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is one of the most commonly used non-pharmacological techniques for lower back pain relief, chiefly due to its cost-effectiveness and lack of side effects. (9)
2. Massage
Massage therapy could provide short-term relief from acute, subacute, and chronic back pain. (10) Frequent massages may be costly, but getting a massage once a month can be effective and affordable as well. It is important to select the massage best suited to your problem.
3. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
Also known as psychoeducation, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help relieve chronic back pain and also can lead to improvements in functional status and behavioral outcomes.
Each factor that contributes to the pain can be treated using focused CBT. It is also recommended to start CBT therapy early to help prevent and treat chronic pain. (11)
4. Chiropractic treatment
Chiropractic treatment is performed by a chiropractor and focuses on your joints and surrounding soft tissues. The chiropractor utilizes hands-on techniques to provide relief from joint pain and therefore restore normal functioning.
5. Physical therapy
Physical therapy involves educating a patient on various strengthening and stretching exercises to help relieve the pain. Manual therapies and modalities such as ultrasound, ice and heat applications, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may also be used.
6. Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy utilizes various exercises that help improve your strength and flexibility and consequently reduce your back pain. It is recommended that you perform the exercises under the supervision of a physiotherapist.
Ways to Relieve Back Pain at Home
The following home remedies and self-care measures can help prevent and treat your back pain:
1. Exercise regularly
Certain exercises promote proper posture and increase muscular support for the spine. (12) Some exercises that can help reduce the risk of injury by strengthening your back include:
- Low-impact aerobics, such as cycling, Pilates, swimming, and tai chi, can help improve blood flow and nutrient delivery to the soft tissues in your back, which will loosen your stiff muscles and promote quicker recovery. It is suggested to perform 30 minutes of such moderate physical activities every day. (13)
- Core-strengthening exercises, such as climbing the stairs, weightlifting, hiking, partial abdominal crunches, planks, squats, and bridges, help strengthen your muscles, improve functionality, and provide joint stability.
- Stretching exercises, such as yoga and Pilates, can open up your stiff back muscles and improve your overall flexibility. Limber muscles are less prone to injuries.
2. Consume a healthy diet
Avoid high-inflammatory foods such as sugars, trans fats, and processed foods to prevent back pain.
3. Avoid smoking
Nicotine is known to inhibit blood flow to your back. Additionally, it is seen that smokers often experience back pain and recover slower than non-smokers. Therefore, it is best to abstain from smoking.
4. Maintain a healthy body weight
A meta-analysis revealed obesity and overweight as contributing factors to lower back pain. (14) As a heavy body contributes to increased pressure on the spine, maintaining a healthy body weight can help reduce your back pain.
5. Check your posture
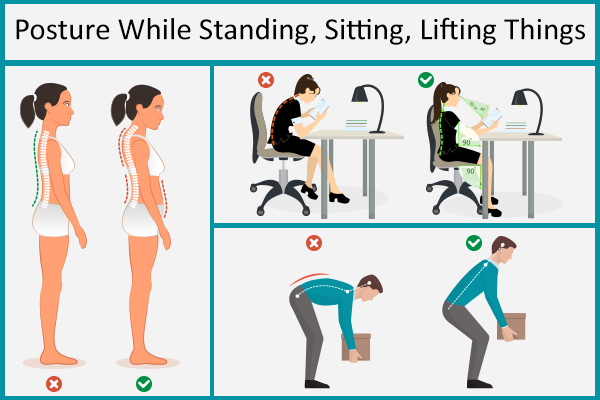
It is vital to maintain correct posture at all times to prevent undue strain on the spinal joints and muscles. Here’s what you can do:
- While standing, keep your feet at shoulder-length apart, and knees slightly bent, and shift your weight mainly to the balls of your feet. Allow your arms to hang loosely on your sides, pull your shoulders back, and tuck your stomach in. When standing for a long time, alternate your weight between your toes and heels or between one leg and the other.
- While sitting, support your arms with the chair arms. Sit with a straight back and the sole of your feet parallel to the ground. The knees should be bent at roughly a perpendicular angle. Also, avoid keeping a thick wallet or papers in your back pocket.
- When lifting things, take the support of your legs rather than your back. Keep your back straight and avoid bending or stooping forward. Use your feet while turning as well, rather than twisting your back. Moreover, refrain from lifting and twisting at the same time, such as while shoveling snow. It is also advised to avoid frequent twisting and bending.
6. Stay in motion
It is necessary to avoid long periods of inactivity. Take a short walk during your break, especially if you have a desk job. Additionally, move around and avoid eating your lunch at your desk.
You may also use gadgets to improve your posture or set reminders for movement after an extended period of tablet or mobile use.
7. Avoid wearing heels
High-heeled sandals such as stilettos and pumps, can alter the alignment of the spine, hips, and lower back. This often results in fatigue of the back muscles and pain.
8. Manage your stress
Stress management can have a short-term effect on physical functioning and severity of pain. (15)
9. Strike a balance between rest and activity
People with severe back pain are recommended bed rest for a couple of days, after which they must slowly resume their regular activities. Exerting your back while it is already in pain will only aggravate the pain. So, it is important that you gradually ease your body into the normal routine.
10. Select a comfortable mattress
A medium to firm mattress, which supports your shoulders and hips without giving in and keeps your spine straight, can help prevent back pain. Extremely soft or hard surfaces can aggravate the pain. Moreover, it is advised to refrain from sleeping on your stomach.
11. Avoid sudden movements
Avoid jerky and sudden movements, especially when getting out of your bed in the morning. Try to roll to your side and push yourself up with the help of your hands while shifting your legs to the bedside, instead of bending from your waist while getting up.
Most-Asked Questions About Back Pain
Can kidney pain be confused with back pain?
Due to the location of kidneys at the rear of your body, pain in the kidneys can be mistaken for back pain. It is recommended to seek medical help to identify the real source of pain and for a proper diagnosis.
Can lower back pain indicate a serious condition?
Lower back pain is one of the first symptoms to occur when prostate cancer metastasizes and forms lesions. In rare cases, the pain can stem from infections in the area, especially those that occur in the wake of recent surgery or tuberculosis.
Can back pain result from a urinary tract infection?
A urinary tract infection causes redness and irritation in the lining of the urethra and bladder. The infection can further cause pain in the lower abdomen, pelvic area, and even lower back, often increasing your need to urinate. Therefore, pain in the lower back and sides may indicate a urinary tract infection.
Does abdominal bloating cause back pain?
The buildup of air or gas in the abdomen can make the area heavy, rigid, and tensed. This kind of bloating often causes discomfort and pain, which might radiate to the back.
Moreover, due to the supportive function of the lower back, a bloated stomach may cause increased pressure in the area, resulting in pain.
Final Word
Excessive reliance on painkillers to cope with persistent or recurrent back pain can have negative health outcomes in the long run. So, it is best to diversify your treatment plan by including multiple therapies, exercises, and self-care measures under the guidance of your doctor.
Read Further to Prevent Back Pain at Work
This chapter is part of the Back Pain: Reasons, Risk Factors, and Treatment series.
In the next chapter, you can read about the ways to build strength and improve hip mobility to avoid back pain at work.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


