In this article:
A jammed finger is an injury to a finger joint called the proximal interphalangeal joint.
Small ligaments support this joint, and straining or overstretching of these ligaments can also lead to jammed fingers. This usually happens when a lot of force is applied to the hands.
Some common incidents of jammed fingers may result from:
- Sports injury
- Pressing the finger against a surface
- Overstretching of the ligament of the finger
- Automobile accidents
- Putting excessive weight on the hand
- Getting the finger stuck in a drawer or door (1)
A jammed finger may result in pain and the inability to bend, straighten, or grip with the finger. A person can also experience loss of motion and tenderness in the finger.
The anatomy of the finger joint is complex, and several types of injuries can result in permanent problems if they are left undiagnosed or untreated.
A jammed finger can be very painful to deal with and hence should be treated on time. It can take more than a few days to completely heal, but if there is no fracture, it can be treated at home. (2)
Some Ways to Treat a Jammed Finger
Here are some measures you can take to treat a jammed finger at home.
1. Implement RICE therapy
What is RICE? Well, we’re not talking about the edible grain. RICE is an acronym for rest, ice, compression, and elevation, which are beneficial for patients with injuries such as a jammed finger.
Rest
Rest helps prevent further injury and can aid in healing. Any kind of injury requires rest for quick healing. If you continue to do activities with the finger, the injury will worsen, which can lead to increased inflammation or pain. It can also lead to further injury such as a fracture.
Make sure that you’re resting your affected finger to avoid any jerks or other risky movements. (3)
Ice and compression therapy

Ice and compression work together to reduce swelling and pain. When you suffer from a jammed finger, you can apply an ice pack to the affected area.
Ice can be applied intermittently during the first 24–48 hours, typically for 15–20 minutes as often as possible, using a plastic bag or towel.
It should be noted that you should not apply ice directly to the skin without first wrapping it in a cloth or towel. (4)
Injuries can be compressed using a splint, elastic bandage, or a Jones compression dressing in cases with severe swelling. The Jones dressing consists of 4 layers: layers 1 and 3 are cotton batting, and layers 2 and 4 are elastic bandages.
Note: Experts suggest that after 48 hours, periodic warmth, such as a heating pad, can be applied for 15–20 minutes to relieve the pain and expedite healing.
Elevation
If you have a jammed finger, make sure that your finger stays elevated. This is done to ensure proper blood flow to reduce inflammatory symptoms such as swelling and pain.
Elevating the injured area above the heart during the first 2 days helps drain edema fluid with the help of gravity, reducing swelling.
Elevation also makes sure that the waste materials from the finger are eliminated, which is helpful for healing the finger. When you’re sleeping, you can elevate your finger by putting it on a pillow. (5)
2. Apply turmeric paste

It is a very well-known fact that turmeric has good anti-inflammatory actions, which can help reduce any pain and swelling that is caused by a jammed finger.
Turmeric is rich in a chemical compound called curcumin, which helps in improving blood flow to the affected area, hence improving the symptoms of inflammation.
To apply turmeric to a jammed finger, all you have to do is mix it with coconut oil to create a paste, which can then be applied to the injured part. (6)
3. Consume ginger tea

One of nature’s best agents for relieving inflammation is ginger. A jammed finger can come with a lot of pain, and hence, ginger can come in handy to alleviate such symptoms.
Ginger is abundant in a chemical compound called gingerol, which has anti-inflammatory properties. This makes ginger a great agent for controlling symptoms such as pain, redness, and swelling.
All you have to do is drink ginger tea, which you can make by boiling ginger in a cup of water and then drinking it twice a day. (7)
4. Apply aloe vera or drink aloe vera juice
Aloe vera is another natural compound with anti-inflammatory actions. It can help reduce the stiffness or soreness that comes with a jammed finger.
Aloe vera is a good remedy for promoting healing by repairing the skin. The best way to use aloe vera is to gently massage aloe vera gel on the affected area at least twice a day. Drinking aloe vera juice is also a great way of expediting healing. (8)
5. Wear a splint
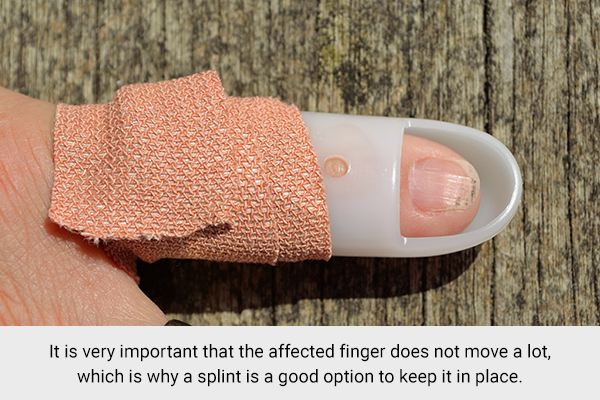
If an injury is determined to be unstable, a splint could be the most appropriate treatment option. A splint is generally described as an external device that immobilizes a joint or injury and is usually constructed from plaster.
It is very important that the affected finger does not move a lot, which is why a splint is needed to keep it in place. It will help prevent aggravating the injury.
Make sure the splint you’re wearing is not too tight or too loose. If it is very tight, it will inhibit proper blood circulation. The duration of wearing a splint depends upon the extent of the injury and speed of healing. (9)
Note: According to experts, it’s crucial to differentiate between a splint and a cast. A cast is a rigid application of plaster that encircles a joint or fracture to provide immobilization, whereas a splint is not circumferential. Because of their restrictive nature, casts are not used immediately after an injury when soft tissue swelling is common.
Exercising a Jammed Finger
To avoid frequent occurrences of jammed fingers, it’s important to keep our hands healthy through exercise. However, it’s crucial to wait until the pain has subsided before attempting any exercises.
Here’s what you can do:
- Sit on a chair beside a table.
- Place the forearm on the table with the elbow bent and the palm facing down, allowing the wrist and hand to hang over the edge.
- Hold a light weight in the hand.
- Slowly bend and straighten the wrist, raising and lowering the hand while keeping the forearm secure on the table.
- Do 3 sets of 10 repetitions, taking a 1-minute break between each set.
- Increase the weight as the exercise becomes easier.
Note: It’s recommended to consult with your orthopedic specialist before starting these exercises.
Why is exercising good for preventing injuries?
Exercise plays a crucial role in preventing injuries, as it can enhance tissue resilience and tolerance to the forces experienced during vigorous activities.
When recommending exercise, two principles should be considered regardless of the indication:
- Patients should exercise according to their needs, physical ability and must be completely involved to achieve the desired outcome.
- Exercise stimulus should be adequate to encourage the body to adapt to a higher level of function, but not so intense that it leads to injury.
Note: While this article doesn’t focus on exercises, it’s worth noting some contraindications to exercise, which include:
- Suspected acute coronary syndrome (blockage in the arteries that supply blood to the heart)
- Third-degree heart block (when electrical signals that control the heartbeat are disrupted)
- Uncontrolled hypertension
- Acute heart failure (sudden and severe worsening of the heart’s ability to pump blood)
Additional Tips for Managing a Jammed Finger
If you’re suffering from a jammed finger, keep the following points in mind:
- Remove any jewelry from the injured finger.
- Stop or limit activities that are causing pain, for example, typing, using vibrating tools for work, or playing an instrument or sports.
- Take anti-inflammatory pain medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve), as per requirement.
- Once pain and swelling recede, the finger can be reconditioned by exercising the joint, for example, by making a fist or squeezing a stress ball.
When to See a Doctor
Although a jammed finger resolves itself after a few days, you should go to the doctor if you experience the following signs and symptoms:
- Crookedness or deformation of the finger
- Numbness in the finger
- Fever
- Increased swelling
- A snapping, grinding, or popping noise was heard at the time of the injury
- Changes in the shape and color of the finger
Moreover, if you have diabetes, problems caused by a jammed finger can be serious, so have yourself checked by your doctor right away.
Most-Asked Questions About a Jammed Finger
Can tea tree oil be used to manage a jammed finger?

Tea tree oil is an anti-inflammatory agent and hence can be useful to treat pain and other inflammatory symptoms in the affected finger.
To use tea tree oil, apply it to the jammed finger and gently massage it in circular motions. Doing this at least twice a day can help the pain and swelling to go away. (10)
Is olive oil useful in treating jammed fingers?
Olive oil is also a very good treatment for jammed fingers because of its anti-inflammatory properties. It also promotes healing by repairing and moisturizing the skin.
Massaging the jammed finger with olive oil can improve blood circulation in the area, which will reduce stiffness. Doing this even for only a few minutes can aid in the management of a jammed finger.
Using warm olive oil is also an excellent option. (11)
What causes a jammed finger?
Any injury to the joint in the middle of the finger can cause a jammed finger.
How do I know if my jammed finger injury is serious or not?
To determine the severity of a jammed finger, a doctor will conduct a physical examination to assess factors such as finger position, movement, pain, and swelling. Additionally, X-rays are commonly taken to aid in the diagnosis.
Should I tape a jammed finger?
Taping a jammed finger may provide some support and stability, but it is generally not necessary and should be avoided if there is significant swelling or if it causes discomfort.
Final Word
A jammed finger is a common injury that can cause pain and discomfort. It is essential to take appropriate measures to treat it on time to prevent permanent damage.
Home remedies such as rest, ice therapy, compression, elevation, and natural anti-inflammatory agents such as turmeric, ginger, and aloe vera can be used to ease the pain and swelling.
In severe cases, wearing a splint can help immobilize the finger and prevent further injury. However, if the injury is severe or shows no improvement, it is essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Was this article helpful?
- YES, THANKS!NOT REALLY


